Table of Contents
- Crawled Pages
- Issues by Importance
- Issues by Category
- Top 3 Fixes Recommended by cognitiveSEO
- All Issues
- Title
- Headings
- Thin Content
- Duplicate Pages
- Duplicate Descriptions
- Canonical Pages
- Unsecure Content
- Malware
- Images
- Social
- Hreflang/Languages
Create a Site Audit Campaign
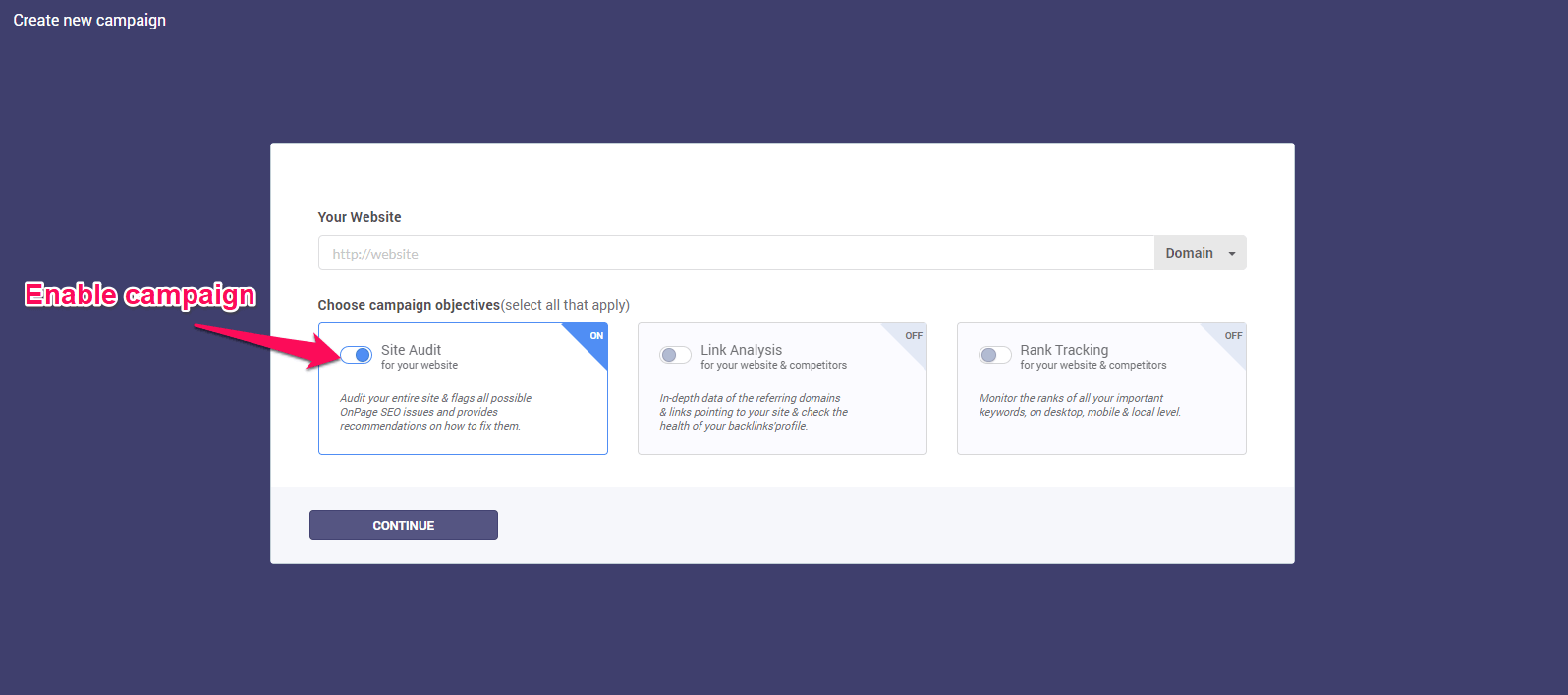
In order to create a campaign, please click on Start your first SEO campaign, right on the main Dashboard. The wizard will open and you’ll be able to select the Site Audit module and click Continue.
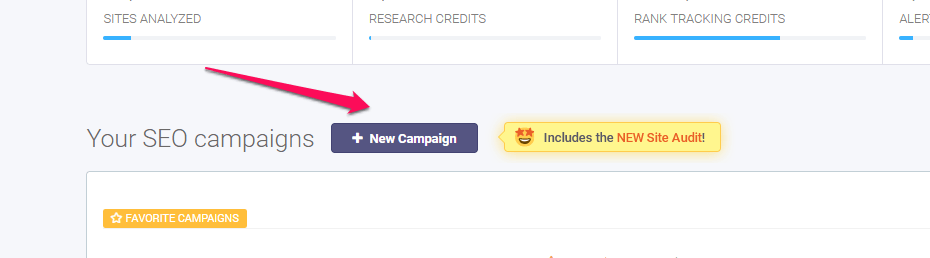
In case you have other campaign created and you want to create another one click on the +New Campaign button above your list of campaigns:
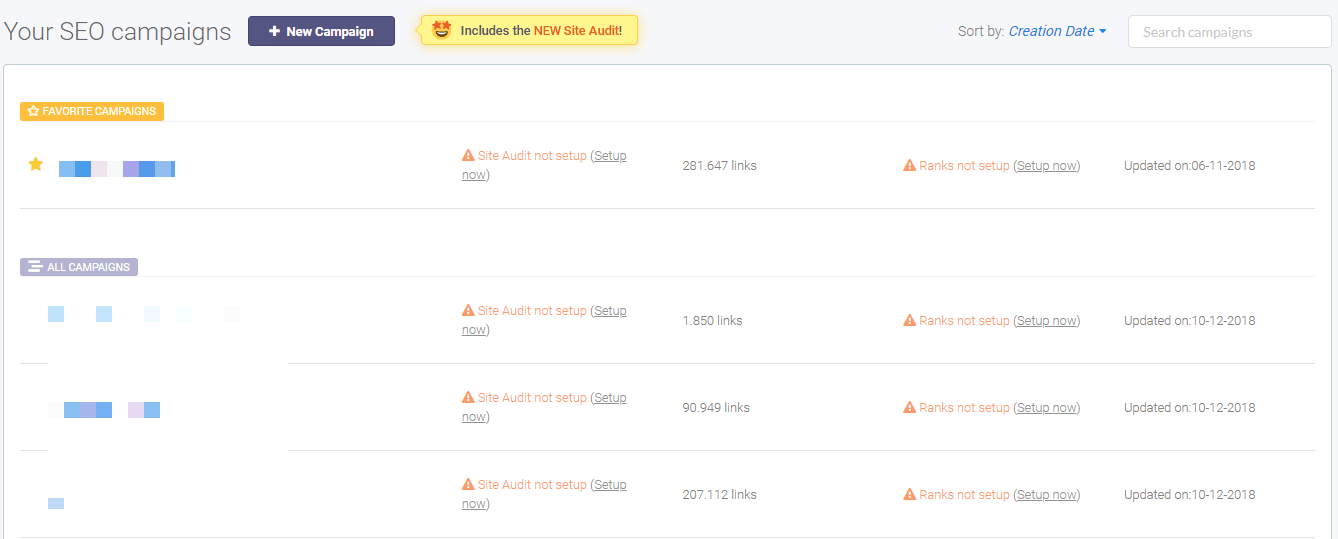
On the SEO dashboard are all the campaigns created by a user. For each campaign, there is the option to run the Site Audit, inBound Link Analysis, Rank Tracking and more. It is displayed what actions are performed on every campaign, be it on-site analysis, link analysis and so on.
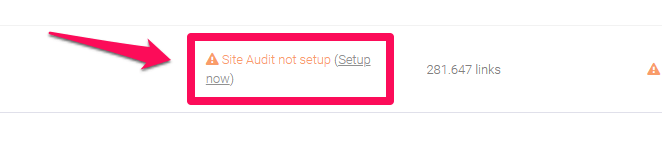
To run the Site Audit for a campaign, go to the desired campaign click on Setup now.
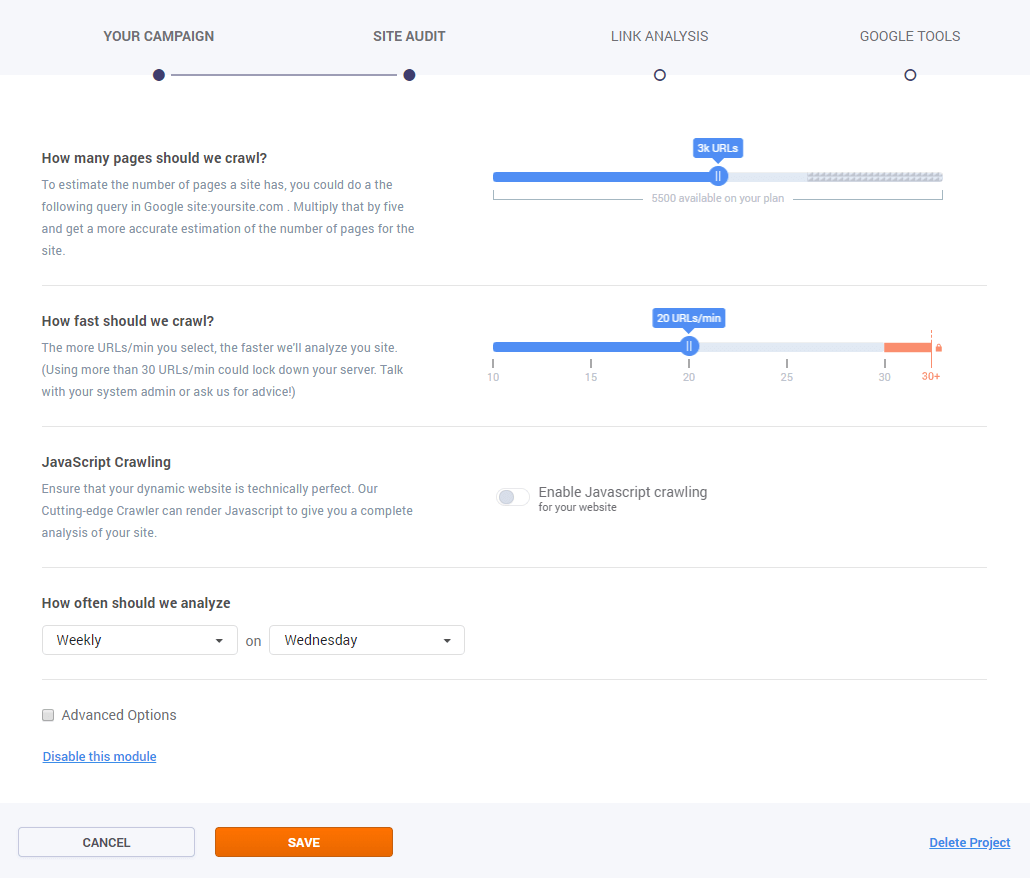
The Campaign creator will open to select the settings you’d like for your website. There are the next available options:
- the number of crawled pages: 100 – unlimited;
- the time needed for crawling: 10 URLs/min – 30 URLs/min;
- the option to enable JaveScript crawling;
- the desired elements for crawling
- the recrawled period.
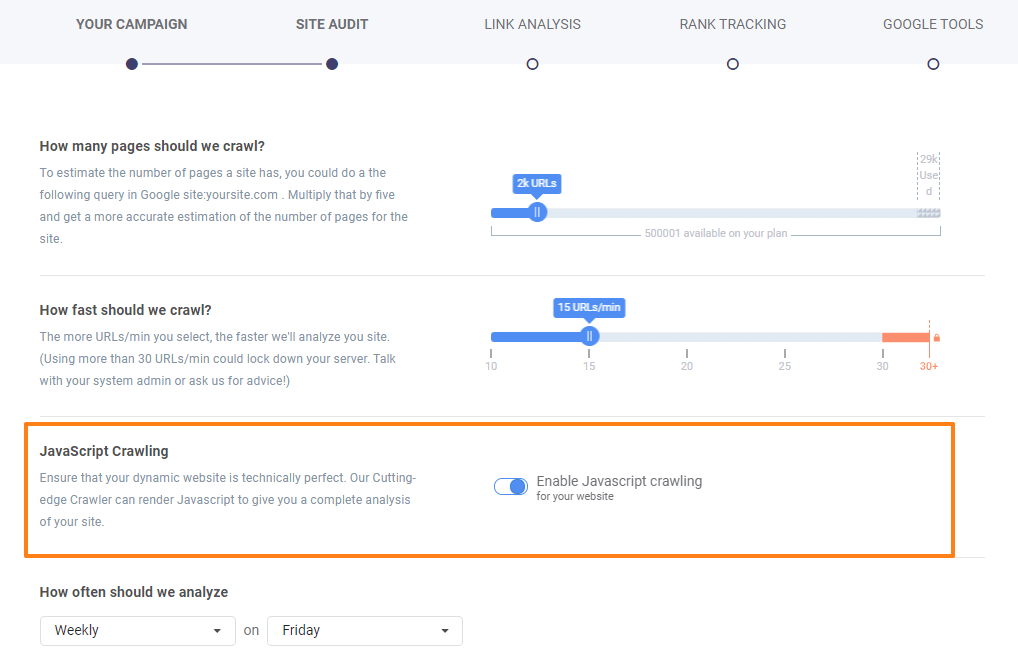
JavaScript Crawling
Use JavaScript crawler to analyze sites that are using JavaScript. Check the box to Enable JavaScript Crawling and verify if your dynamic website is technically perfect and there are no errors.
Advanced Options
There are Advanced Options for having a more accurate analysis of a website.
.
Crawl Sources
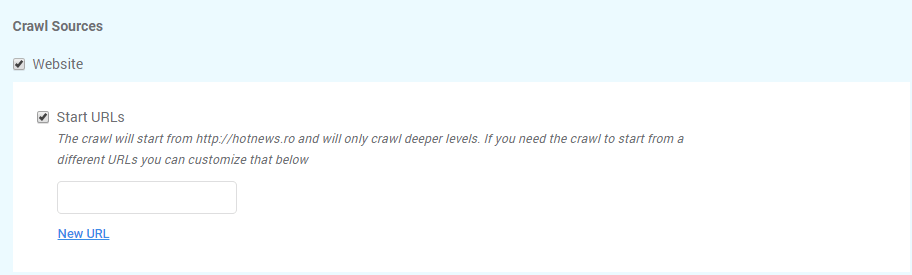
The default setting for cognitiveSEO is to crawl your website. There are two other options available, so it can be configured to also crawl XML Sitemap URLs, and/or a provided URL List.
Selecting the Crawl website option the tool will crawl all web pages to discover new URLs until every page on the website is crawled. In case you want to crawl pages that start with a different URL you can choose that by selecting Start URLs.
cognitiveSEO has the option to Crawl Sitemaps, which allows you to have a more in-depth audit. Please make sure that after you select the box for Sitemaps you chose the desired option for including the Sitemap in the Site Audit. You can either let the tool discover it automatically, enter the URL or uploaded from your computer.
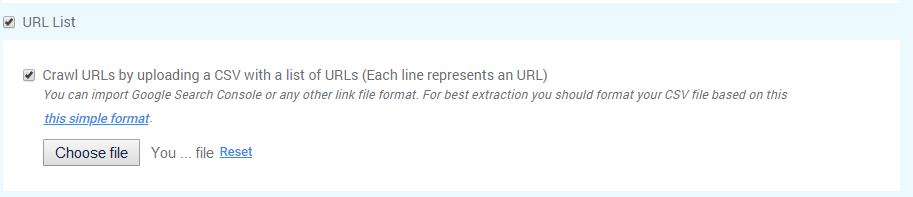
The third option, Crawl URL list can be performed by uploading a saved file from your computer. Make sure you select both boxes to save your options.
Typically URL Lists are used when you DON’T also crawl the website and are used to crawl a specific area or section of the site.
What to Crawl
Deciding what to crawl can be a little be tricky. There are lots of elements that you can choose from:
- Internal sub-domains have the next format: subdomain.example.com. One common example of subdomains is blog.example.com. If you want to analyze and crawl the subdomains that you have (in case you do) you need to select the box.
- Non-HTML files are image files, PDFs, Microsoft Office or OpenDocument files, and audio or video files stored on the webserver.
- CSS files are used to define a style for a single HTML page. CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheet and is used by web pages to help keep information in the proper display format.
- External links are links that point out to another website. For example, other websites/URLs linked to your website are external links. They send the visitor from your site to another site.
- Images. Here are included all the images in different formats, that are added to your website’s media library.
- Nofollow links have the nofollow tag that indicates to search engines that the links added on a page shouldn’t be followed by them.
- Noindex pages are pages blocked by the webmaster to appear in search engines. All the pages that have a noindex meta tag in the page’s HTML code, or by returning a ‘noindex’ header in the HTTP request can be crawled by the Site Audit if you select the box.
- JavaScript files contain all the HTML HEAD and BODY objects in the tags of an HTML page.
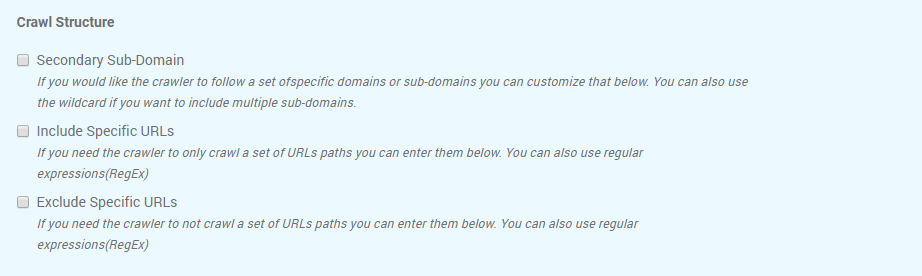
Crawl Structure
The Crawl structure has other options for crawling website’s data from specific sources, such as secondary sub-domain, or specific URL path. In case there are URLs that you don’t want to crawl, you can select the last box and let the tool know it should crawl all the links expect the selected path.
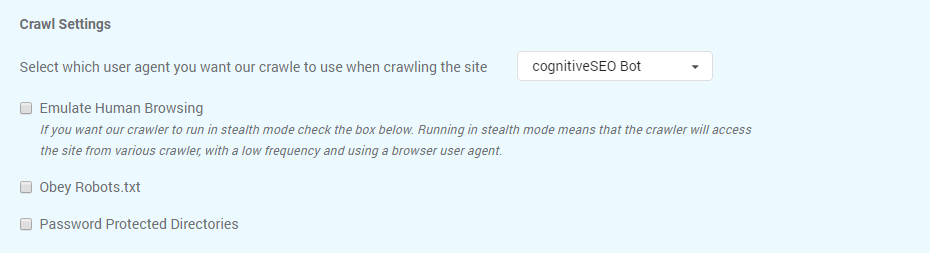
Crawl Settings
Select the settings that fit you for the website you want to audit, by looking at Crawl Settings and decide the method used for crawling.
You can change the user agent for crawling from the list available on cognitiveSEO:
- Applebot
- Bingbot
- Bingbot Mobile
- Chrome
- cognitiveSEO Bot
- Firefox
- Generic
- Google Web Preview
- Googlebot
- Googlebot – Image
- Googlebot – Mobile Feature Phone
- Googlebot – News
- Googlebot – Smartphone
- Googlebot – Video
- Internet Explorer 8
- Internet Explorer 6
- iPhone
The Emulate Human Browsing option means that the crawler will access the site from various crawlers, with a low frequency and using a browser user agent following a natural user behavior.
A robots.txt file is used to issue instructions to robots on what URLs can be crawled on a website. If you decide to Obey Robots.txt then all the URLs will be crawled according to the robots.txt file.
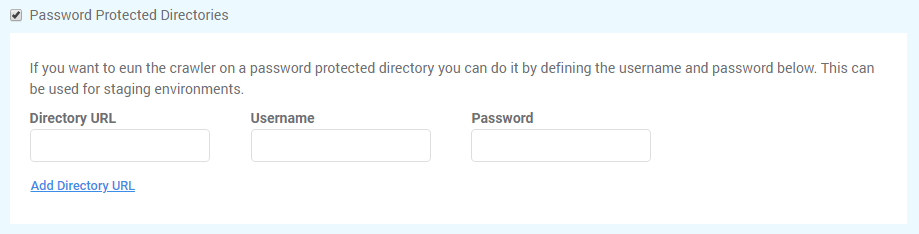
Use Password Protected Directories if you to run the crawler on a password protected directory you can do it by defining the username and password below. This can be used for staging environments.
Then the tool will crawl your site and you’ll be able to see the result on the Site Audit Overview Dashboard.
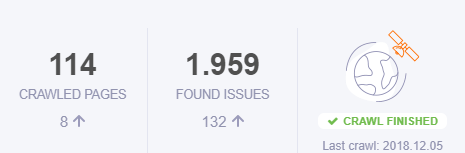
The Site Audit Overview shows you the number of pages crawled plus the existed issues for the website you’ve added. There is a notification that says if the crawled is completed and when will be the next recrawl.
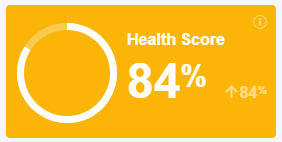
For every site that runs the Site Audit analysis, you can see the Health Score, which shows from 1-100 % the degree to which a website is optimized for SEO. It is desired to have a higher score as possible. The higher the score the better. The Score is calculated based on both your errors and warnings. That means if you have fewer errors and warnings then the score will be higher.
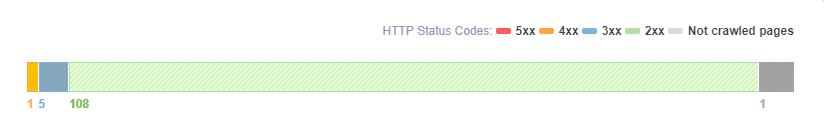
Crawled Pages
Besides the score, you can see a chart bar with the number of Crawled Pages with a specific error to understand the internal issues for your webpage. Besides these 5 types of errors, you might see a category for Not crawled pages. If you found yourself in this situation, it might be because of the settings you managed when you first created your campaign or there might be a problem with those pages. You can contact support and find the specific problem for that website.
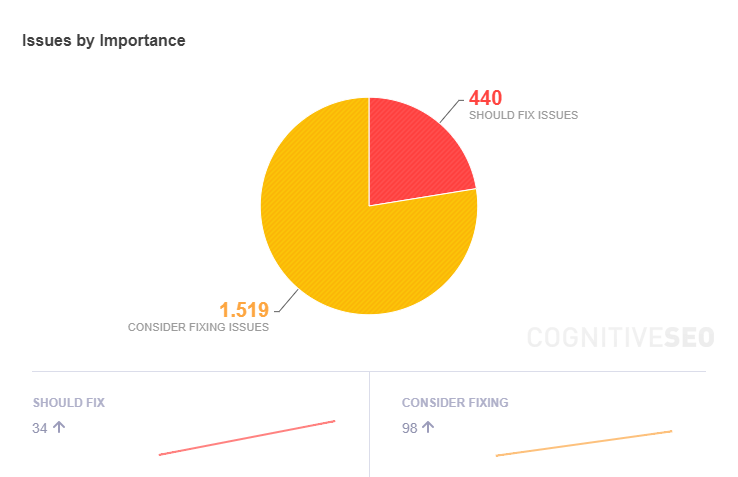
Issues by Importance
On the Overview dashboard, there is the Issues by Importance chart that shows you which are your major issues that you need to take care now and which one of them might not be so important as you thought. By looking at this chart you can have a better understanding of what needs to be fixed right now, and what should be left on the sideway for the moment.
Below the chart, there is a clickable area where you can access the issues that need fixing and the number of issues that appeared after the last recrawl.
Issues by Category
The second chart from the Overview dashboard is the Issues by Category, where you can understand the nature of your issues. The website used in the example below has most of its issues in the content area and none problem regarding performance. Each of these categories can be found in the menu and can be accessed afterward for a deeper analysis.
Just like in the previous chart, below you can see the number of issues from each category that appeared after the last recrawl.
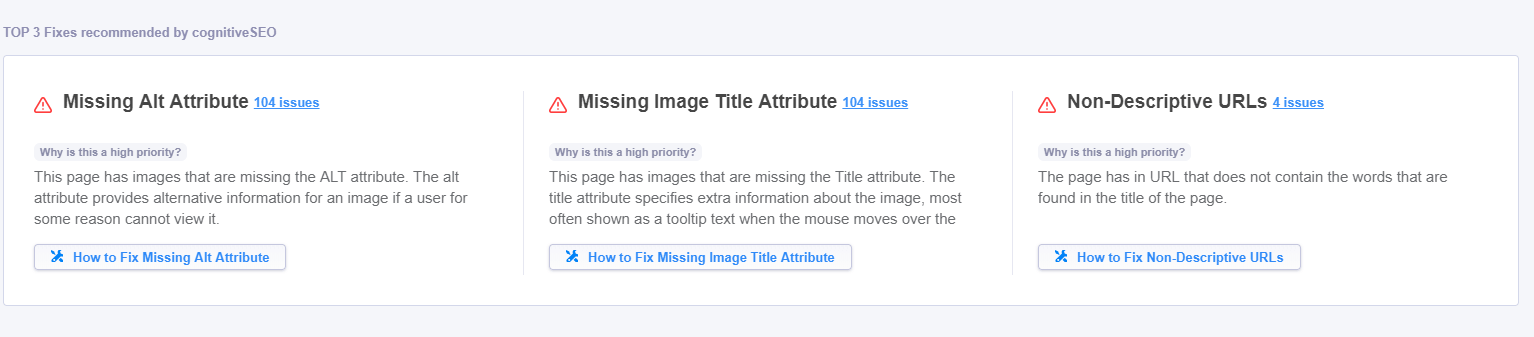
Top 3 Fixes Recommended by cognitiveSEO
Since a website can have lots of issues, some more important than other, you can see the Top 3 fixes recommended by cognitiveSEO. After the tool analyzes your website it gives you some insights and tips for the first 3 problems that can be related to the architecture of the website or content area, like the example you can see below, or they can be related to the performance of the website and so on.
To resolve every issue from this stage you’ll have to click on the How to – button and get directions to the specific section in the tool. For example, if you want to fix missing alt attributes, then you’ll be redirected to Content » Images. Here you’ll see the list of all the pages that have this issue. Furthermore, you’ll have to go to that page on your website and add alt-attributes to your images. At the next recrawl, if you managed to add the missing all description and didn’t forget to add it to the newly uploaded images, then you won’t have this issue displayed.
Remember, if you managed to resolve the issues that you have here, you need to apply the same actions in the future for the same elements that you add on site.
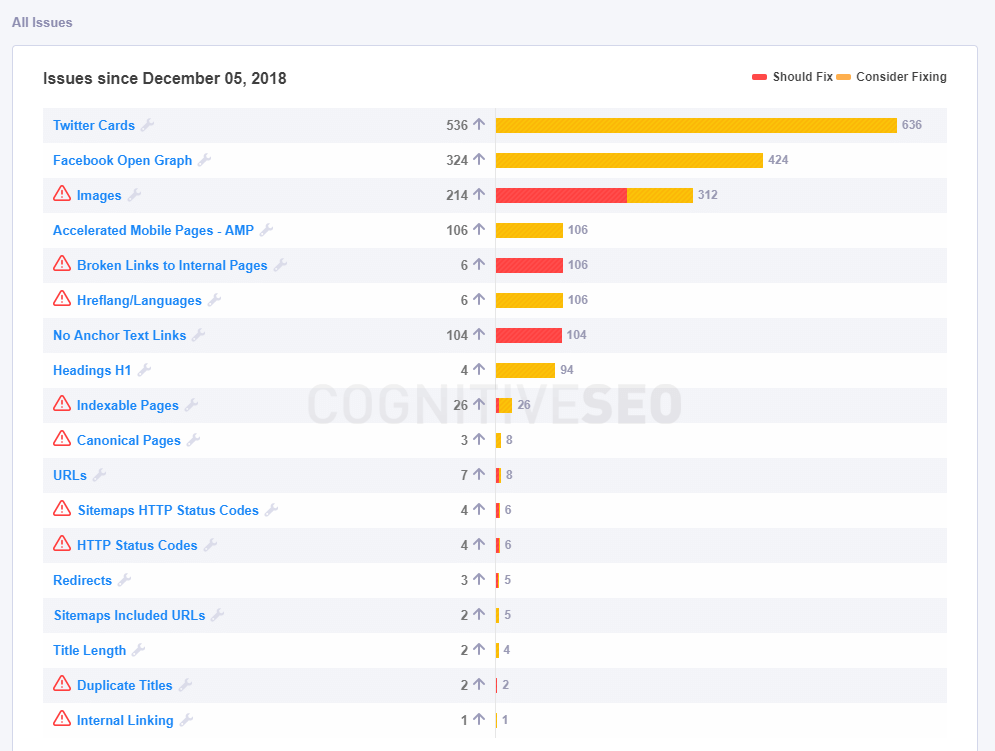
All Issues
The rest of your website’s issues can be found in the final list on the Overview dashboard. Below you can see just an example. There might be different issues for each selected website. Every chart bar is clickable so if you decide to take a look into every specific issue, you can click on them.
.
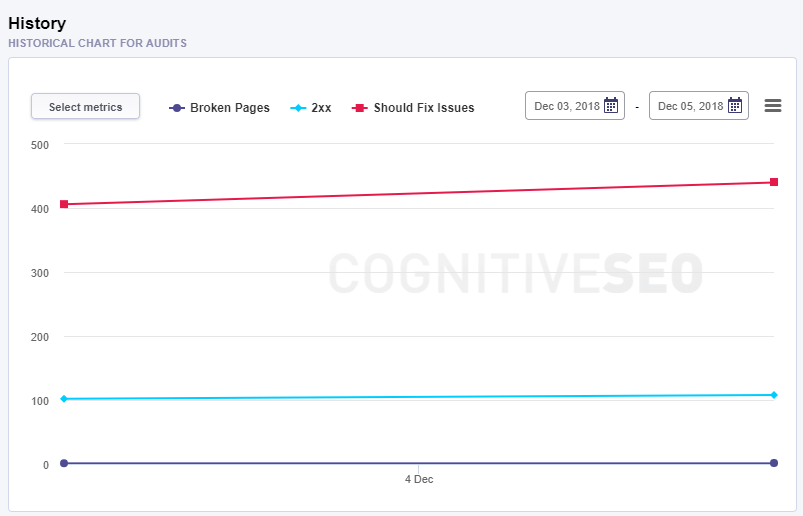
History
Historical Chart for Audits
The evolution for the website can be viewed in the Historical Chart of Audits. From one crawl to another, this chart displays the trend of pages that have improved or have experienced a lot more issues. The data for the audit history can be accessed since the first time you set the Site Audit analysis for that website.
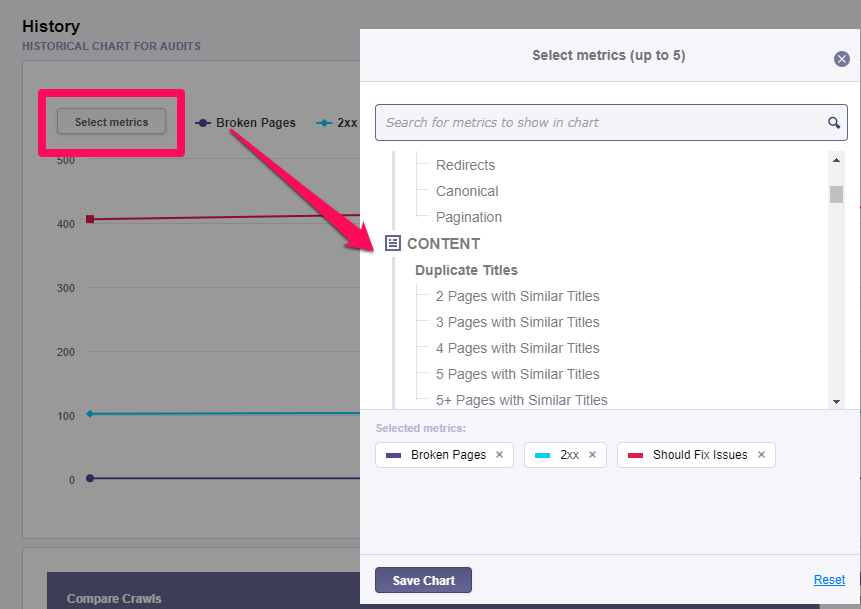
There is the option to personalize this chart with metrics regarding indexability, content, mobile, performance, issues. The limit is set to 5 maximum metrics displayed on the graph. The default mode has the next metrics: Broken Pages, pages with 2xx Error Code, Should Fix Issue.
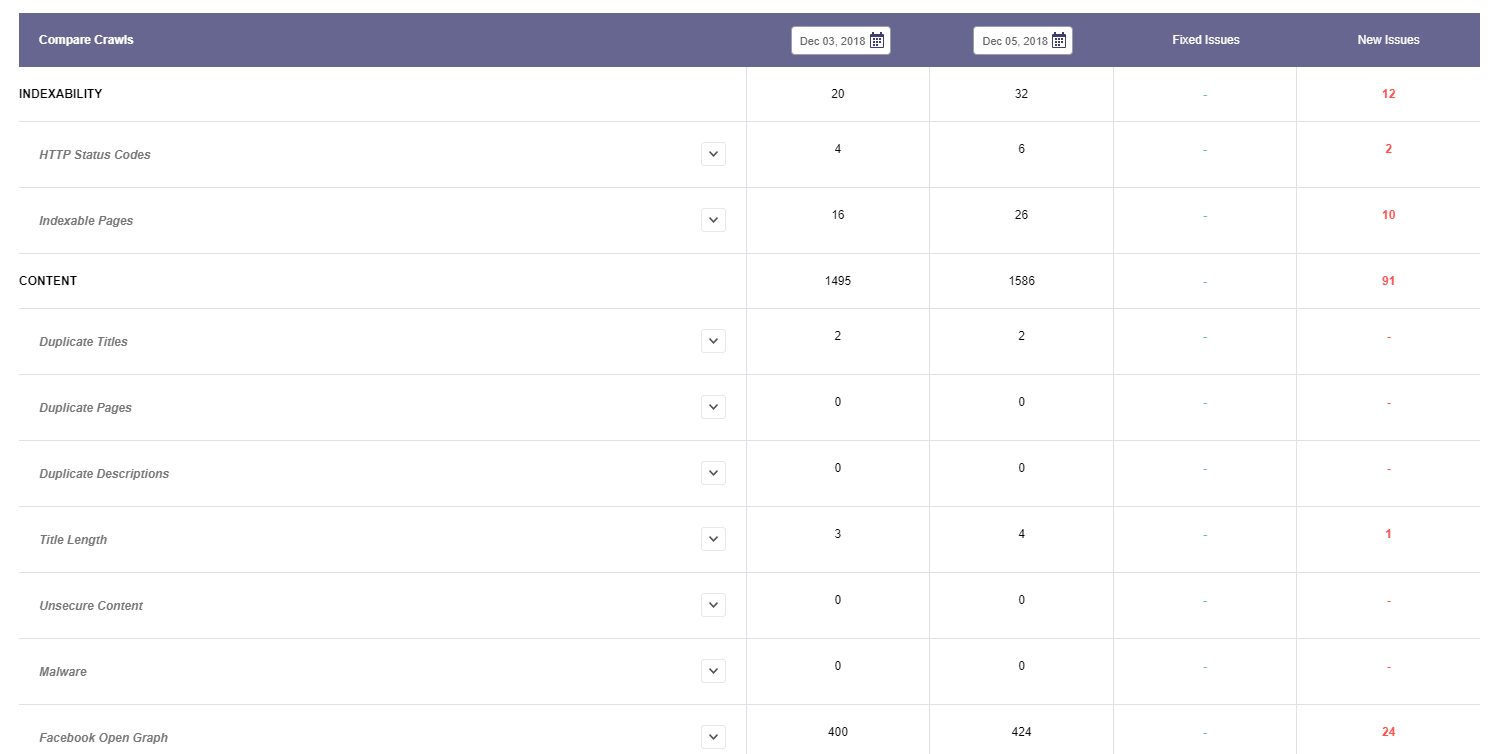
Compare Crawls
The Compare Crawls sheet contains two dates when your website was crawled so you can compare them side by side and see if there are any improvements for your website. You can choose any two dates that you want and are available on the calendar.
The re-crawl is made automatically. When you create a campaign there is the option to select a recrawl once a month, once at two weeks or once per week. Depending on your campaign settings, you’ll be able to select the comparing dates for this chart.
Every single metrics displayed on the Site Audit tool can be found here for comparison.
Indexability
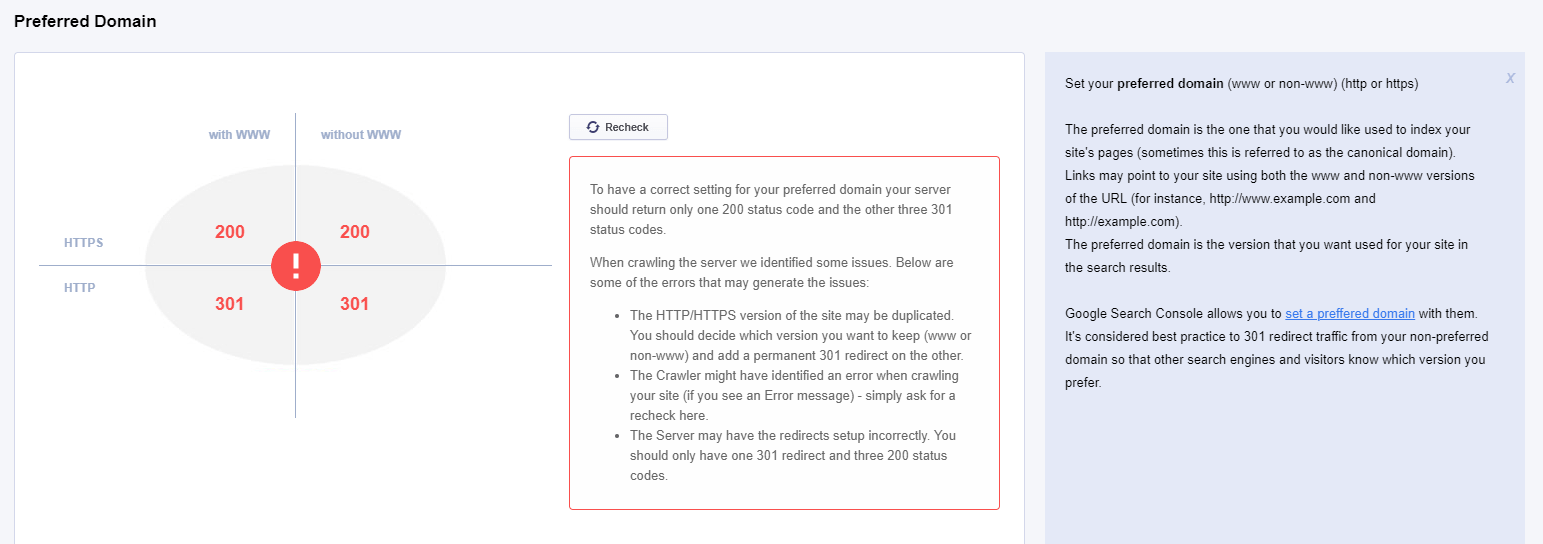
Preferred Domain
Every website might have a www and a non-www version. It is important to have a preferred domain selected in Google Search Console. The Site Audit analyzes your website and sees if you have set a preferred domain or not. The desired situation is to have only one 200 status code and the other three 301 status codes.
There are two situations once you get here. Your status is ok and this is the desired situation. You can see that the website used in our example has the 200 code for the www version for HTTPS, and for the rest of them has 301 redirects. The preferred version is the URL that starts with https://www, and the rest of the https://, http://www and http://www are redirected to the preferred version.
The second situation when you don’t have a preferred domain. you can see the screenshot below. In this case, you need to go to your Search Console and set there a preferred version of your website.
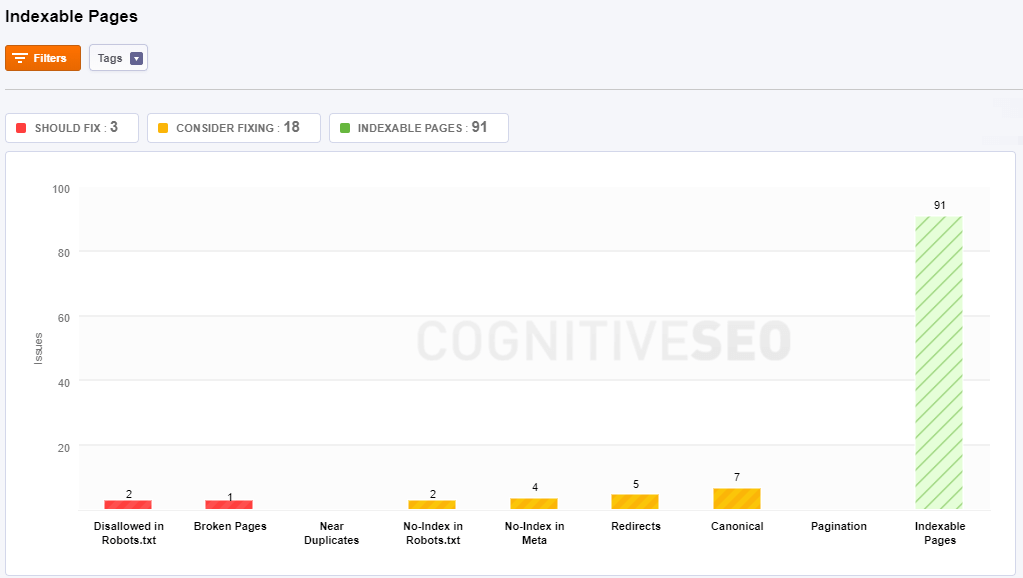
Indexable Pages
Indexable Pages, as the name says it, are pages indexed by search engines (be it Google, Yahoo, Bing, Baidu, Yandex or others). This type of pages is able to receive traffic and links. Here you can see pages that lots of issues regarding indexability, categorized by the gravity of the situation: should fix (red color), consider fixing (yellow color), indexable pages (green color). It is desired to have are many indexable pages and fewer issues that you need to fix, just like in the example used below.
All the pages marked as Disallow in your robots.txt are displayed in the same chart. The “Disallow” tag tells the search engines bots that it should not crawl this page.
Broken Pages have an URL that is linked to other pages. Clicking on this category you’ll see pages that might not be available for lots of reasons. The URL may be broken or the page may have been removed. You can see the source/location of each broken URL.
Pages that have duplicate content are placed in the Near Duplicates category. The content from such a page can be found on some other pages as well.
The pages from the No-Index in Meta category have a special HTML <META> tag that tells robots not to index the content of this page, and/or not to scan it for links to follow. All the web pages placed in this category have non-indexable content that may not be indexed by search engines. These pages may be in the following formats: HTML, Rich Media Files, Video, or Images. Find any issues regarding pages that are not indexed and should be indexed and vice-versa. You should allow the search engine to index only the important URLs, so that these pages can rank highly.
A Redirect sends users (and search engines) to a different URL from the one they originally requested. Here you can see the redirected pages and if there are any problems associated with them.
The Canonical issue will indicate the pages that don’t have the canonical tag placed. If you have duplicate pages you can choose what page to show in SERP by adding a canonical tag.
Pagination is the process of dividing a document into discrete pages, either electronic pages or printed pages. The pagination issues refer to the e-commerce websites with product listings spanning across multiple pages. In case it is correctly set you’ll see here pages that have this problem. It must be treated, otherwise, it can cause serious damages to your website.
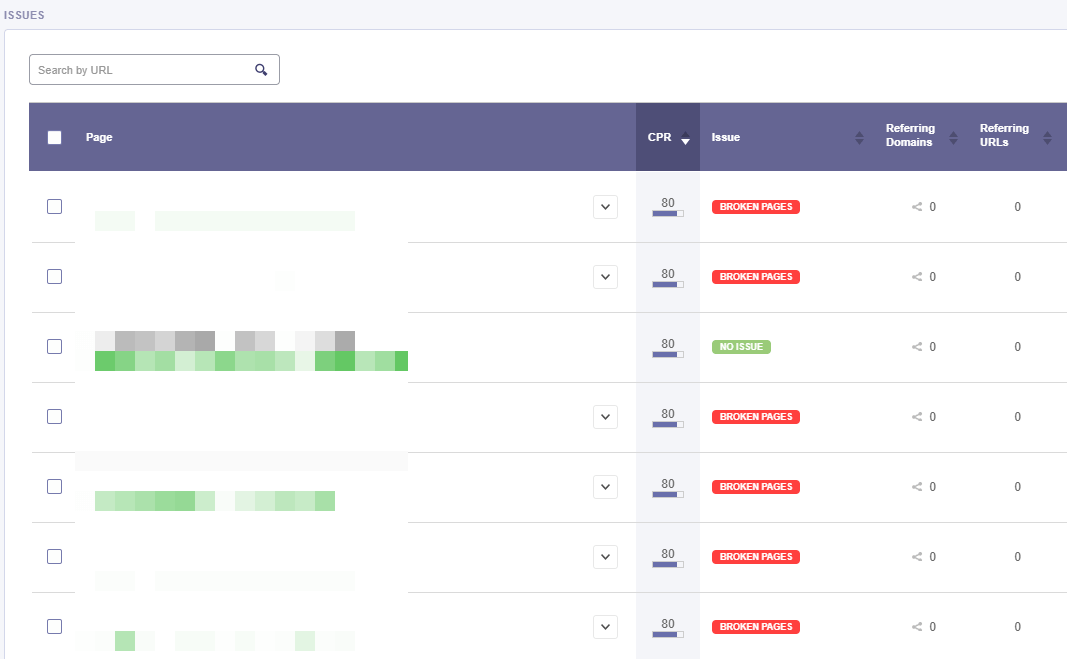
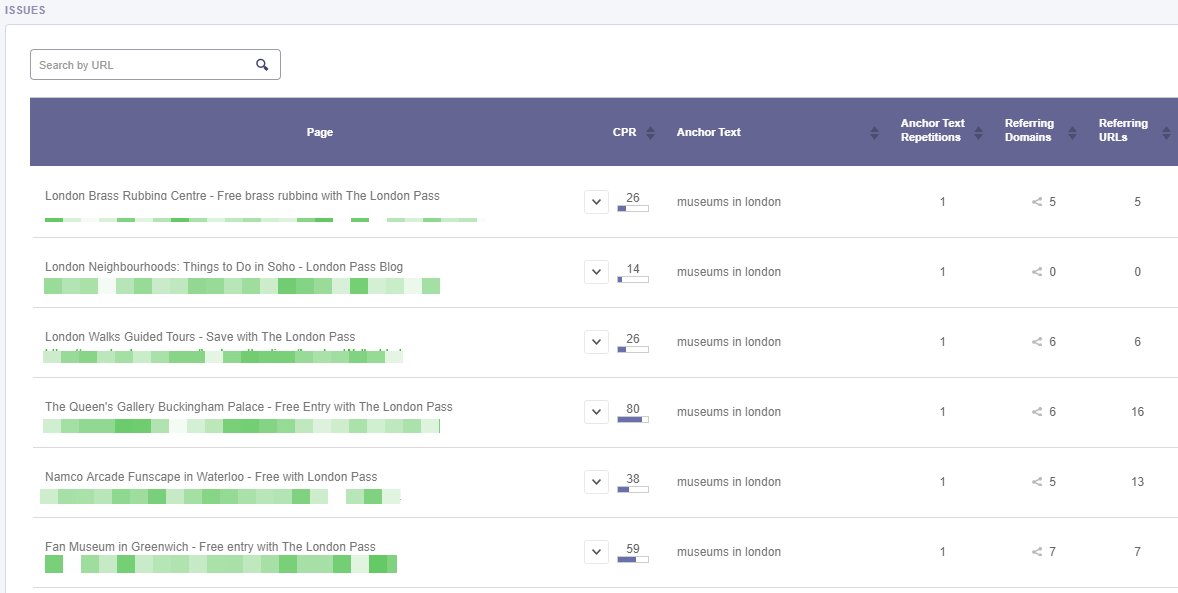
By clicking on any issue from the chart you’ll see the pages in the table below. For each page, it is displayed the cognitiveSEO PageRank (CPR), the number of referring domains and referring URLs. The CPR is a metric that counts the number and quality of internal links pointing to a page to determine a rough estimate of how important that page is. More important pages (like the homepage) are likely to receive more links than other pages on the website.
A referring domain is a domain that backlinks are coming from. A backlink is a link on another website that points to your site. In the chart, you’ll see how many domains are pointing to that specific webpage.
On the same note, there is the number of referring URLs. When a user clicks on a link in a webpage, the user’s browser moves to the specified link. When the browser requests the new page, it sends along the URL of the previous page. This ‘sent along’ URL is called a referring URL.
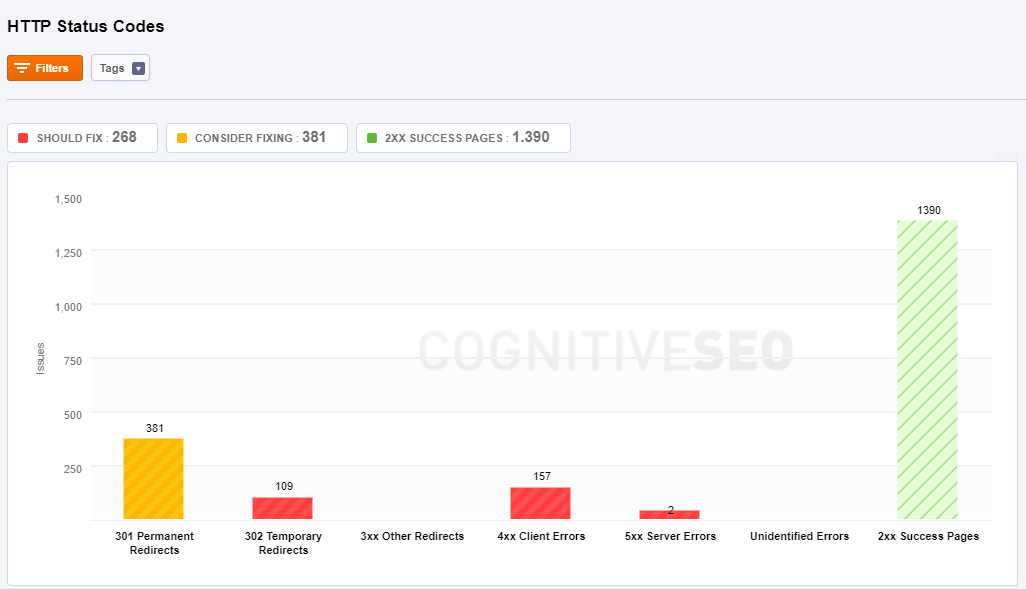
HTTP Status Code
The tool shows you if a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed. There are 5 HTTP response status codes:
- 1xx (Informational): The request was received, continuing process.
- 2xx (Successful): The request was successfully received, understood, and accepted.
- 3xx (Redirection): Further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request.
- 4xx (Client Error): The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled.
- 5xx (Server Error): The server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request.
Depending on the website, in the chart, there is information available for 301 permanent redirects, 302 temporary redirects, 3xx other redirects, 4xx client errors, 5xx server errors, unidentified errors, 2xx success pages.
Pages that have 301 Permanent Redirects to another URL send site visitors to a different URL than the one they originally typed into their browser or selected from a SERP.
302 Temporary Redirects is a code for pages that are temporary moved to a different location. The server redirects the site visitor to the new destination despite the original location still being used for requests.
3xx Other Redirects include 300, 303-307 redirects. All the pages from this category are moved from an URL to a new source. Depending on the error code you can see the state of the redirection.
4xx Client Errors show pages have one of the 4xx class of status code. This means that the user’s request to access this page contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled.
5xx Server Errors show pages have one of the 5xx class of status code. This means that the server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request of the site’s visitor.
All the pages that the tool couldn’t discover the specific code attached, either it is an incorrect setting or a missing code information, are placed in the Unidentified errors category.
2xx Success Pages have a status code that indicates the client’s request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. These pages don’t have an error; are OK pages.
Content
Title
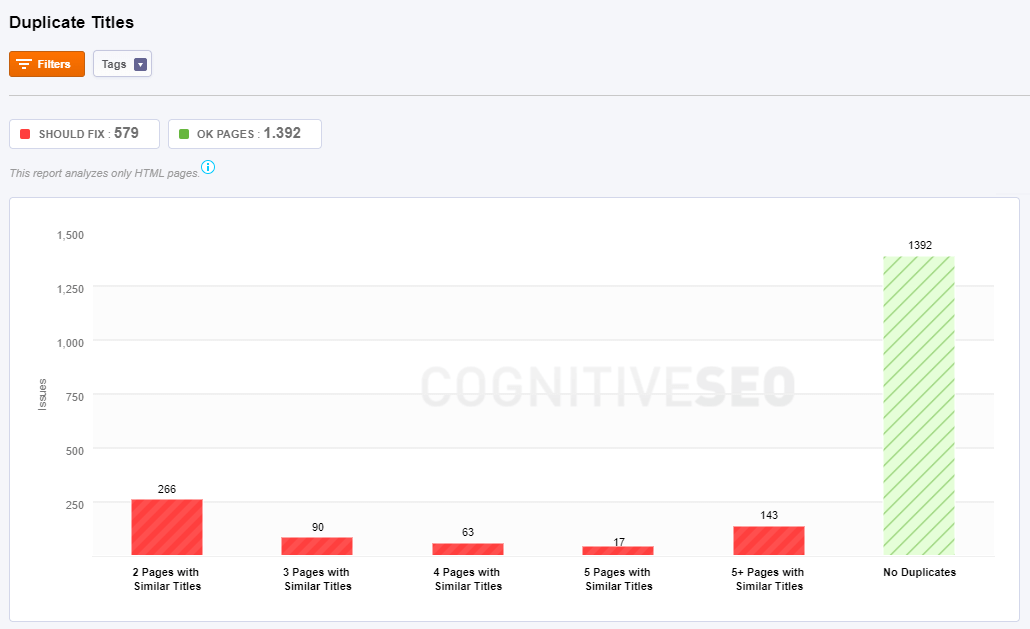
Duplicate Titles
While making a site audit on your website you can evaluate the situation of duplicate content and of course, duplicate title tag issues on your blog pages. As you can see in the screenshot below, there are 5 types of duplicate errors:
- 2 pages that have similar titles: one page that has a similar title to other two pages.
- 3 pages that have similar titles: one page that has a similar title to other three pages.
- 4 pages that have similar titles: one page that has a similar title to other four pages.
- 5+ pages that have similar titles: one page that has a similar title to more than five pages.
Title Lenght
Title Length is important because Google typically displays the first 50–60 characters of a title tag or as many characters as will fit into a 545-pixel display (approximately). If you keep your titles under 60 characters or 530 pixels, then your titles to display properly. If your titles don’t follow the optimal lenght, cognitiveSEO Site Audit will display them:
- Missing title means the page doesn’t have a title and you need to add one.
- Title too short means that the URL in question has a title tag with too few characters. Try following the optimal lenght to attract the user and give more information.
- Title too long (in pixels). You need to add one that is shorter than 530 pixels.
- Title too long (in characters) means the page has a title that is considered too long. Consider adding one that is shorter than 58 characters.
Headings
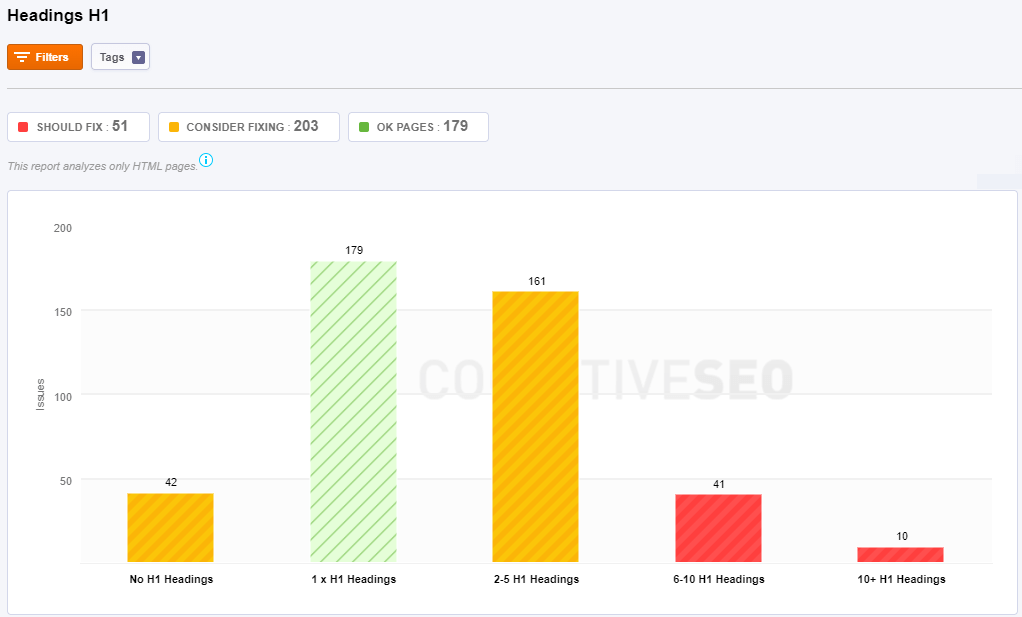
You can evaluate the information for your title headings H1 – H6 and see all the duplicates. Below you can see a print screen regarding the H1 headings which is similar to the other title tags (H2 – H6).
The header tag, or the <h1> tag in HTML, will usually be the title of a post, or other emphasized text on the page. It is recommended that you use the H1 tag for the title of the page and then use H2, H3 and H4 tags for the other sub-titles on the page. Each page on your website should have one H1 tag for the title. If there are any pages that are missing the tag, then the tool will show them in the first category – No H1 Headings.
In case you have more than one H1 on the page, the tool will point exactly the pages that have more than H1 headings on the same page:
- 1 x H1 Headings: two H1 headings on the same page. You have one heading similar with another one on the same page.
- 2 – 5 H1 Headings: there are three, four, five or six H1 headings on the same page. You have one heading similar with other two, three, four or five on the same page.
- 6-10 H1 Headings: there are 7 – 11 H1 headings on the same page. You have one heading similar to other 6 – 10 H1 headings on the same page.
- 10+ H1 Headings: there are more than 11 H1 headings on a single page. You have one H1 heading that is similar with more than 10 H1 headings.
The H2, H3, H4, H5, H6 elements are used to indicate headings whose level of importance is exceeded only by H1. For example, a document may have several H2 elements, all of which share the same level of importance.
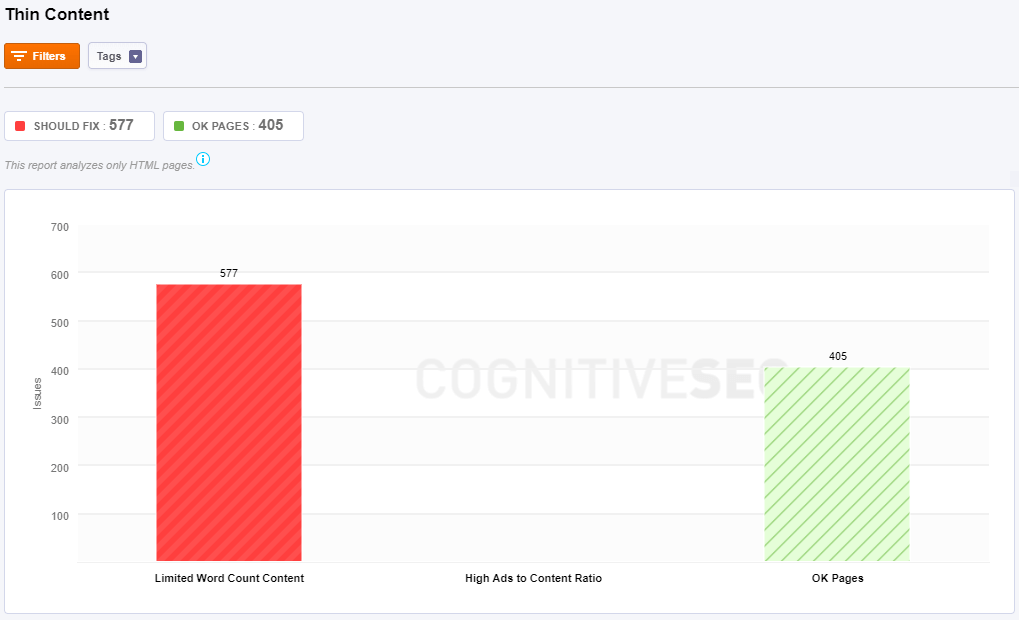
Thin Content
Google defines thin content as “content with little or no added value.”
To fix the issues, Site Audit tool give you some directions you could track. Some of the actions you could take to resolve the pages with thin content are to rewrite the content, improve your site structure or deindex pages with low or no search engine traffic. The issues flagged by Site Audit are:
- Limited Word Count Content means that there are too few words on this page. You should add some text on the page.
- High Ads to Content Ratio means how many ads do you have on a page compared to the ads displayed there. An optimal ratio would be 80 content/20 ads, but that depends very much on how much content do you have, the type of page and so on.
- Ok Pages means there no issue on the page.
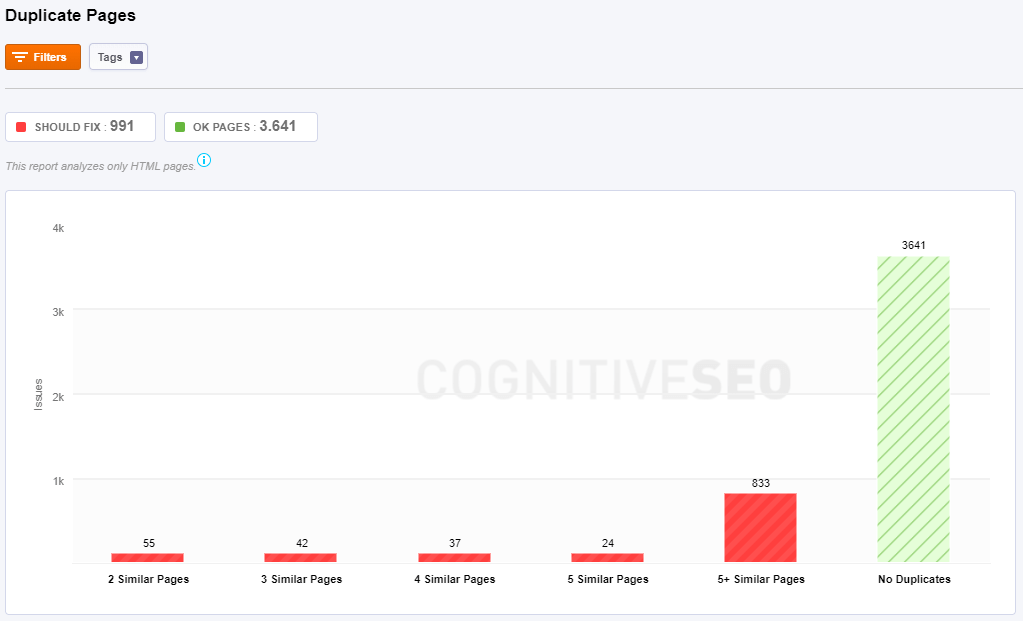
Duplicate Pages
Duplicate Pages refer to the blocks of contents that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar. This type of content can negatively impact your Google rankings as well create a poor user experience when a visitor sees substantially the same content repeated on your site.
Site Audit shows you issues if you have:
- 2 Similar Pages: This page has content similar to the content of two other pages. The boilerplate content was excluded from the analysis.
- 3 Similar Pages: This page has content similar to the content of three other pages.
- 4 Similar Pages: This page has content similar to the content of four other pages.
- 5+ Similar Pages: This page has content similar to the content of more than five other pages.
- No duplicates: no issues.
You can resolve the issues related to duplicate content by:
- Creating 301 Redirect via .htaccess
- Pointing canonical tag to the original content URL
- Blocking via robots.txt
- Deleting/Renaming the incorrect URL.
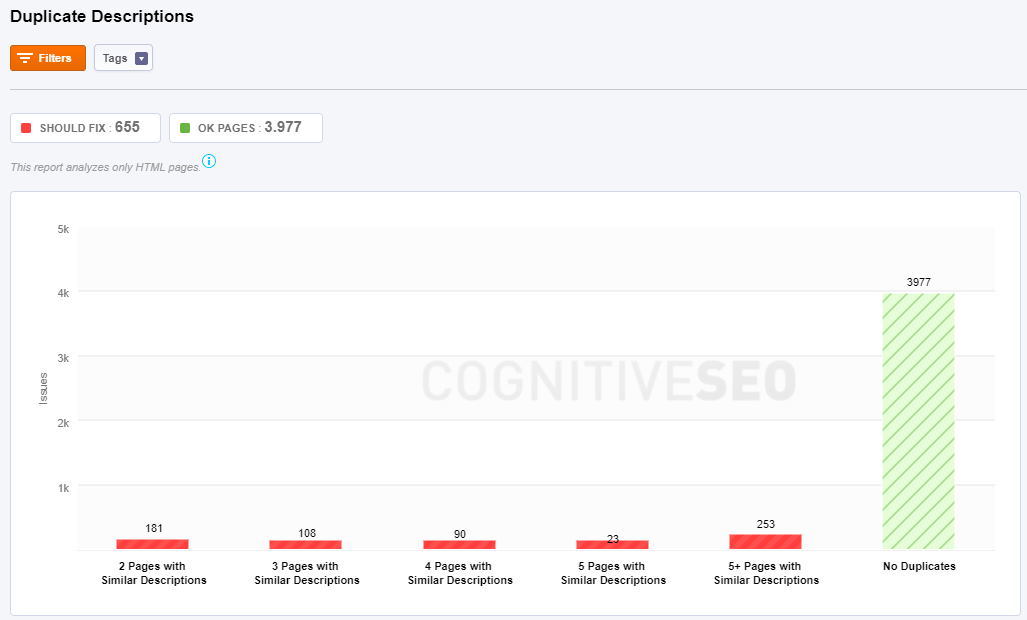
Duplicate Descriptions
Duplicate meta descriptions should usually be avoided. Google says that they’re not a sign that anything is broken, but it is better to don’t have them at all then have duplicate ones. In case you have lots of duplicates you should try to fix them.
The duplicates descriptions show you how many pages have issues:
- 2 Pages with Similar Description: This page has the meta description similar to the meta descriptions of two other pages.
- 3 Pages with Similar Description: This page has the meta description similar to the meta descriptions of three other pages.
- 4 Pages with Similar Description: This page has the meta description similar to the meta descriptions of four other pages.
- 5 Pages with Similar Description: This page has the meta description similar to the meta descriptions of five other pages.
- 5+ Pages with Similar Description: This page has the meta description similar to the meta descriptions of more than five other pages.
Besides this classification, you can see the whole list of links with the issue explained above, plus the meta description that is duplicated.
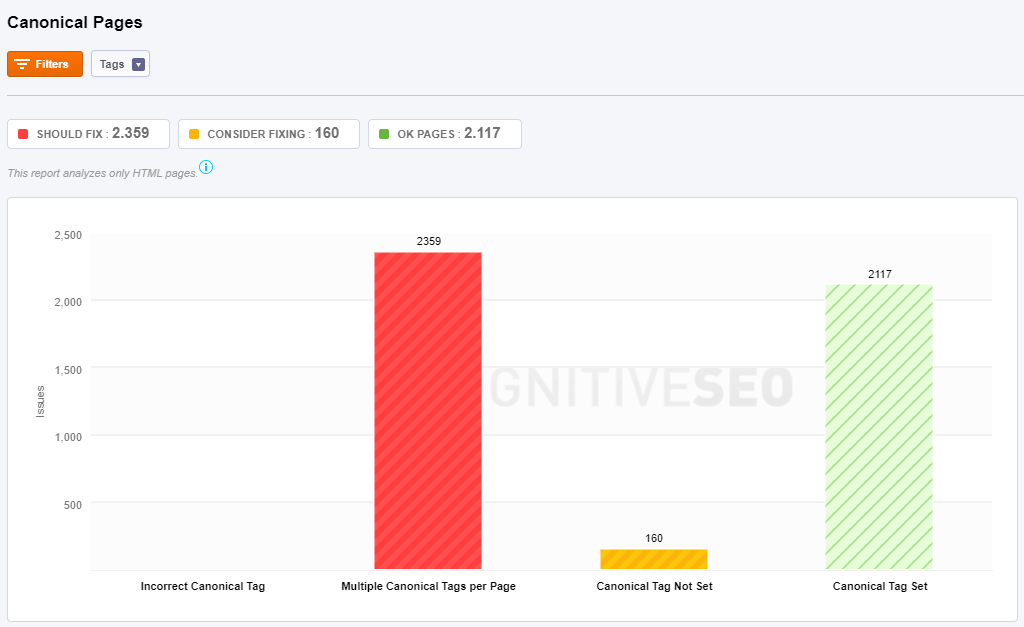
Canonical Pages
A canonical link element is an HTML element that helps webmasters prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the “canonical”, or “preferred”, version of a web page as part of search engine optimization. Choosing a proper canonical URL for every set of similar URLs improves the SEO of your site.
You have three types of issues:
- Incorrect Canonical Tag: If our crawlers don’t first the correct implementation of any canonical tag that you have on your website, then you’ll see the pages here. Indicate the preferred URL with the rel=”canonical” link element: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://blog.example.com/dresses/green-dresses-are-awesome” />
- Multiple Canonical Tags per Page: All the pages from this category have multiple canonical tags. If you have 3 duplicate pages you can choose just one of them to be shown in SERP, by adding just one canonical tag to it.
- Canonical Tag Not Set: There is no canonical tag set for any page classified in this category. If you have 3 duplicate pages you can choose just one of them to be shown in SERP, by adding a canonical tag to it.
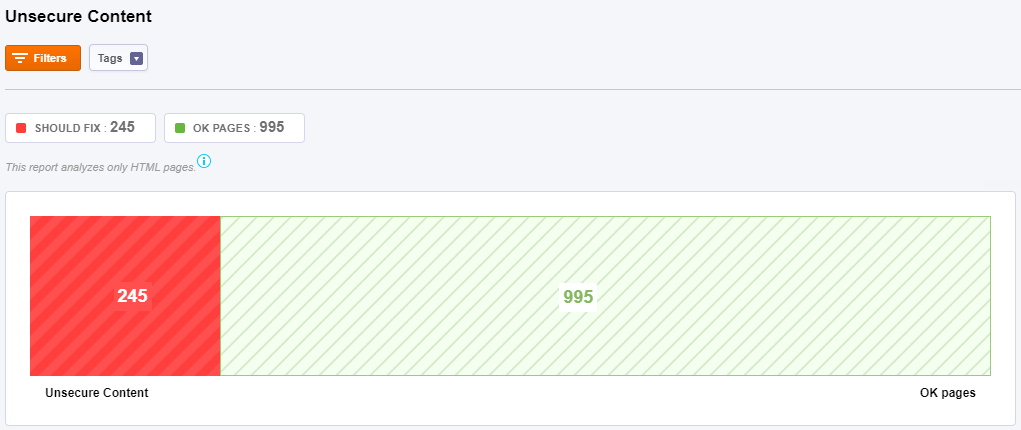
Unsecure Content
Unsecure Content or Mixed Content occurs when initial HTML is loaded over a secure HTTPS connection, but other resources (such as images, videos, stylesheets, scripts) are loaded over an
insecure HTTP connection. Mixed content degrades the security and user experience of your HTTPS site generating Broken HTTPS/SSL Lock Pages.
Here you can see the distribution of your secure pages versus the unsecure pages. This page classified as unsecure content due to the fact that it contains resources from HTTP that are included in a HTTPs site.
Once you find the content being served over HTTP vs. HTTPS, fixing the issue is often as simple as adding an “s” to links – http:// to https://. Before you do that be sure that the HTTP resource is available over an HTTPS connection.
Malware
Malware is any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network. The most common types of malware are considered adware, bots, bugs, rootkits, spyware, Trojan horses, viruses, and worms. Not only is this kind of behavior against Google Guidelines and will get you penalized big time, but it is also illegal. Site Audit shows you:
- Malware Threat
- Social Engineering Threat
- Unwanted Software Threat
- Harmful Application Threat
- URLs Not Checked
If you do not identify the problem and correct the issue Google may de-index your site and you will lose all your search traffic.
This is a quick tutorial that will show you how to take action when your site gets hacked.
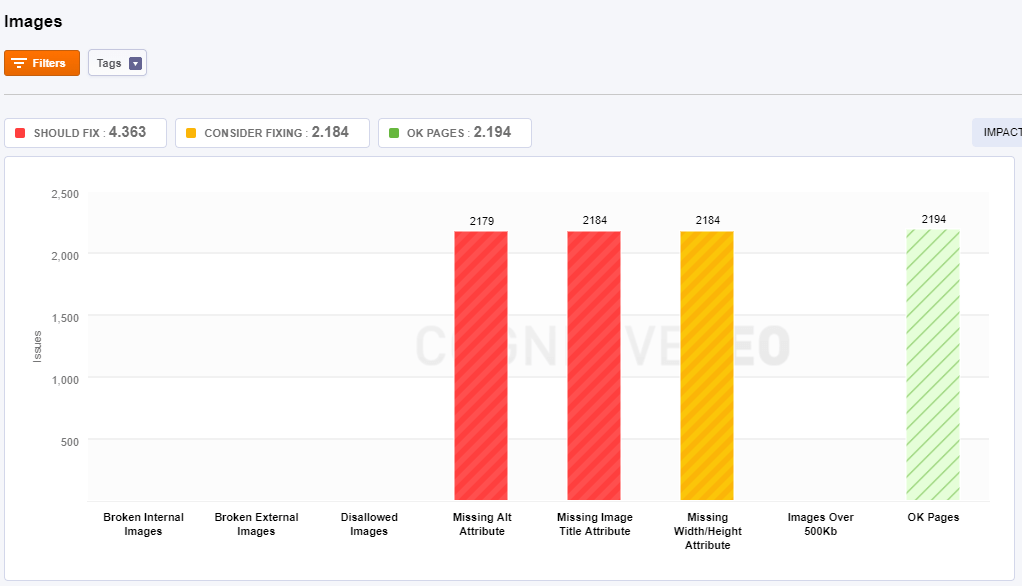
Images
If used correctly, images can boost your SEO as well as your online visibility.
Here are some of the main issues that sites usually have:
- Broken Internal Images – these are images that no longer exist on your site but are still linked to your pages. You need to replace or delete them immediately.
- Broken External Images – these are external images (hosted on other websites) that no longer exist but are still linked from your site. You need to replace or delete their references.
- Disallowed Images – images that are blocked from being indexed by Google.
- Missing Alt Attribute – Images that don’t have a description. ALT tags provide a text alternative to an image. They are a way to “describe” an image to those who can not see the image.
- Missing Title Attribute – the TITLE tag is used for providing supplementary information about the image. The TITLE tag is displayed in a little tooltip when you hover the image.
- Missing Width/Height Attribute – for a faster loading time, you should specify the Height and Width of an Image. They are mandatory, and the browser can still display the images correctly.
- Images Over 500kb – these are images that are slower to load due to their size. Try to optimize them.
Social
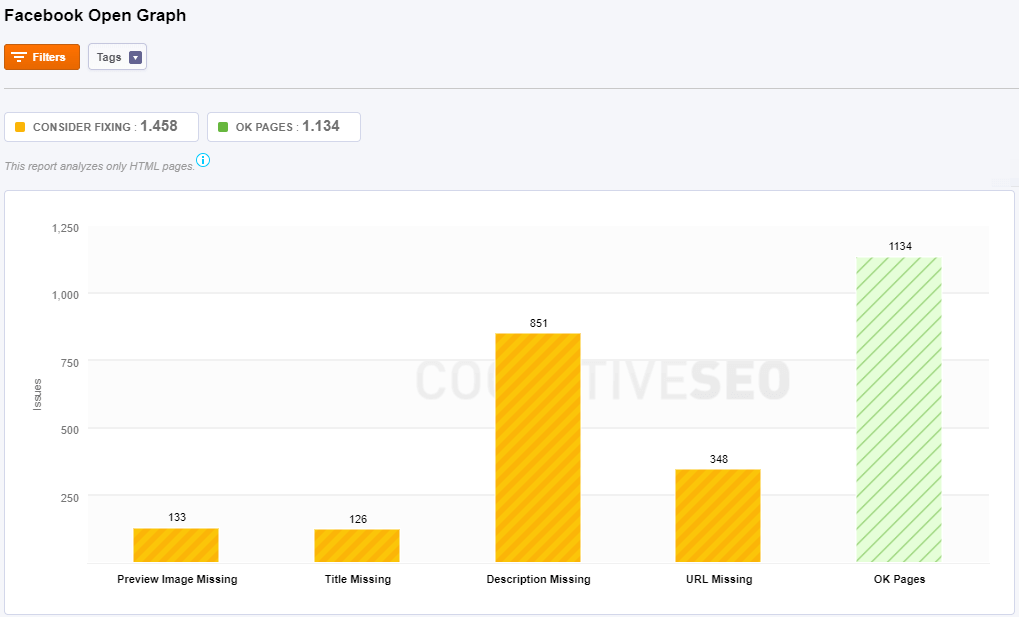
Facebook Open Graph
Here are the issues analyzed by Site Audit:
- Preview Image Missing: It means you have posts shared form your website on Facebook that don’t have a preview image. Mark up your page with Open Graph title tag (“og:image”) to control how your content appears on Facebook. Without it, the Facebook Crawler makes a guess about what title to display.
- Title Missing: Mark up your page with Open Graph title tag (“og:title”) to control how your content appears on Facebook.
- Description Missing: Mark up your page with Open Graph description tag (“og:description”) to control how your content appears on Facebook.
- URL Missing: Mark up your page with Open Graph description tag (“og:URL”) to control how your content appears on Facebook.
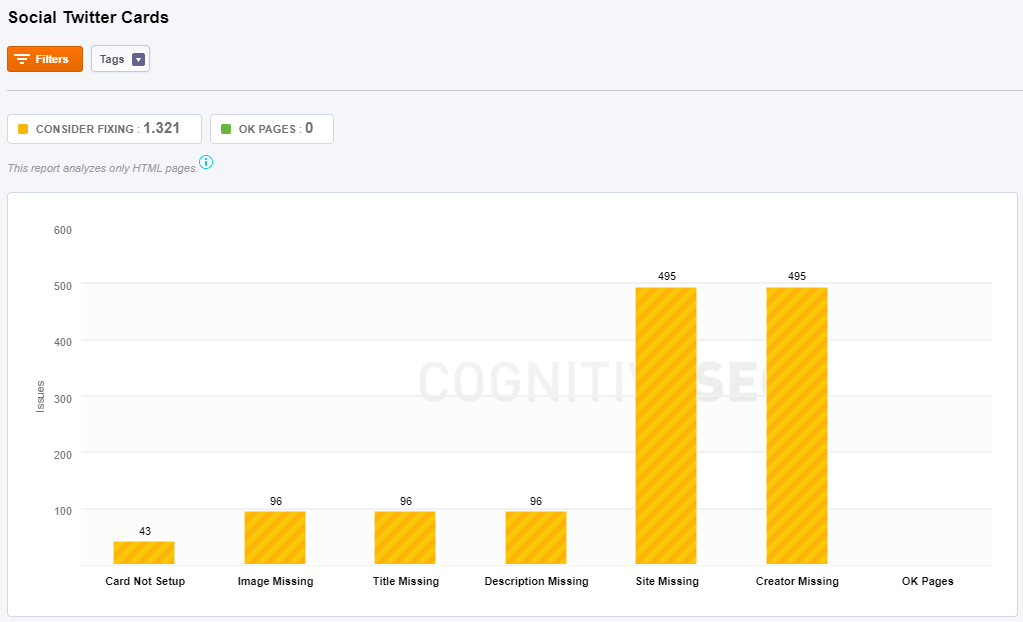
Twitter Cards
- Card Not Setup: Make sure you mark up your page with Twitter card to control how your content appears on Twitter.
- Image Missing: Just like in the case of Facebook Open graph, you have to mark up your page with a Twitter Card image tag (“twitter:image”) to tell Twitter what image to display for your content.
- Title Missing: You should mark up your page with a Twitter Card title tag (“twitter:title”) to tell Twitter what title to display for your content.
- Description Missing: Mark up your page with a Twitter Card site tag (“twitter:description”) to tell Twitter what site to display for your content.
- Site Missing: Mark up your page with a Twitter Card site tag (“twitter:site”) to tell Twitter what site to display for your content.
- Creator Missing: Mark up your page with a Twitter Card content creator tag (“twitter:creator”) to tell Twitter what content creator to display for your content.
Setting the Twitter Cards correctly can help you increase your shares and likes on Twitter.
Hreflang/Languages
Use the hreflang tag for language and regional URLs. If you have multiple language versions of a URL, each language page should identify different language versions, including itself. When you are adding hreflang codes to your web pages, you need to be absolutely sure that you are using the correct country and language codes.
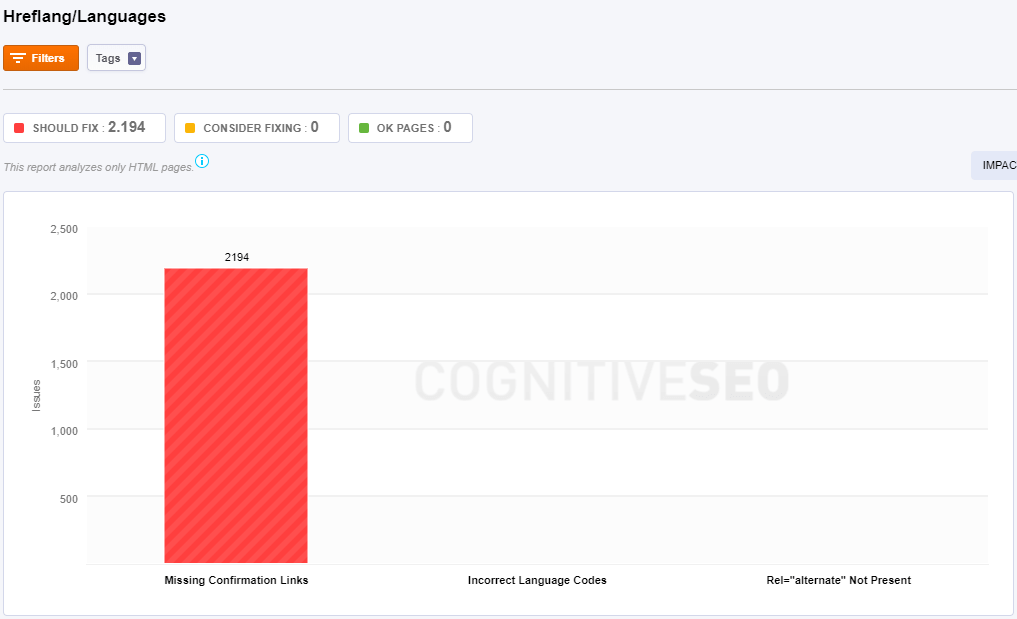
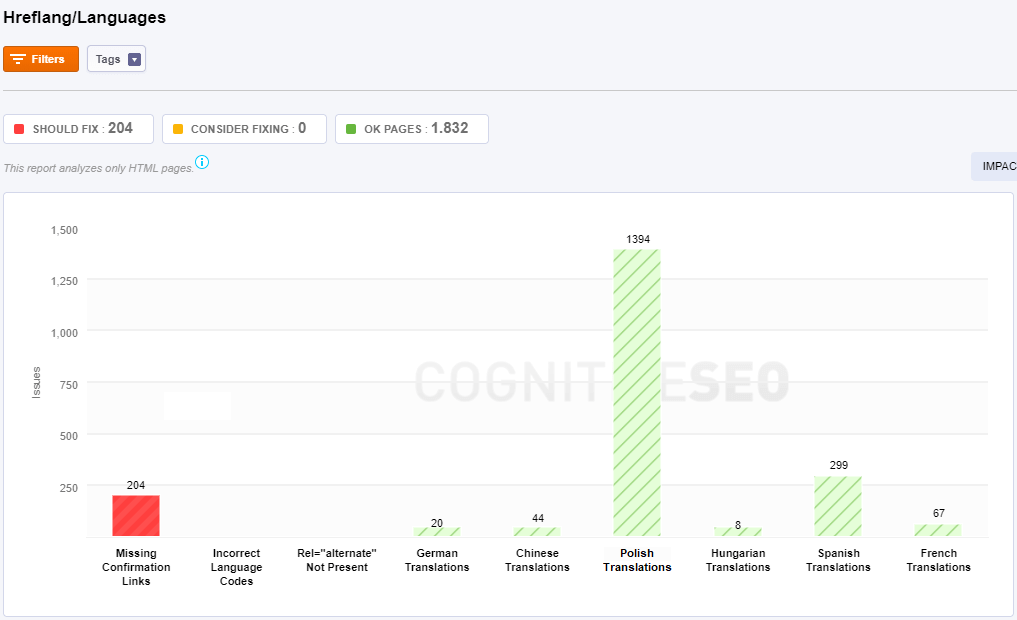
There are multiple scenarios in this section and the tool shows different information charts on each site analyzed. Below you can see two example of charts for two different websites:
The audit shows you the next issues:
- Missing Confirmation Links: All the pages from this category contain an hreflang issue. The hreflang attribute is not implemented in all versions of the site. The hreflang attribute is necessary for setting up a multi-language website.
- Incorrect Language Codes: For each language and location there are some specific codes. In case there are any issues regarding your tags, you’ll be able to see them in this chart. For example, if you create a French-language version of your English-language homepage, you have to tag it as “Français” by using hreflang=”fr”.
- Rel=”alternate” Not Present: The hreflang attribute is not added. You have to add the hreflang attribute for setting up a multi-language website.
- German/Chinese and more Translations: The pages in these categories have the equivalent hreflang.
Architecture
URLs
One of the most important parts of website architecture is making sure users are able to find things quickly and easily on your website. Site Audit makes it easier for you to see if there are are issues regarding site architecture.
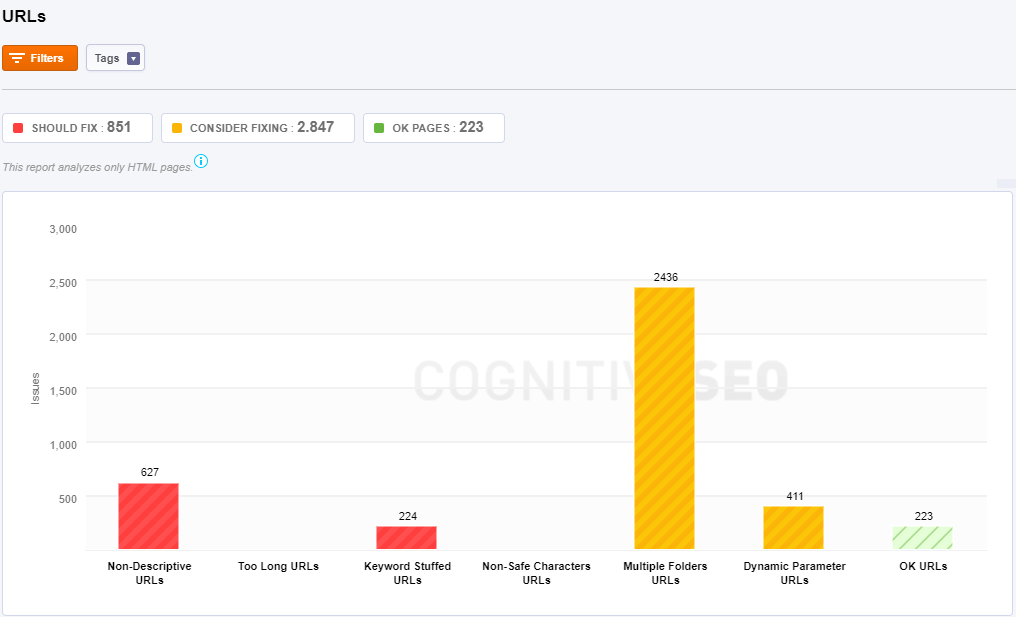
You can see the next issues regarding URLs:
- Non-Descriptive URLs are URLs that don’t match the title or the content of the page. The pages that do not contain in URL the words that are found in the title of the page are included in this category.
- Too Long URLs – Shorter URLs are, generally speaking, preferable. You don’t need to take this to the extreme, and if your URL is already less than 50-60 characters, don’t worry about it at all.
- Keywords in URLs – URLs contain keywords that are repeating at least three times. Consider avoiding keyword stuffing in URLs. iI’s recommended to use keywords from the title of the page when it makes sense.
- Keyword Stuffed URLs – Keyword stuffing and repetition are pointless and make your site look spammy.
- Non-Safe Characters URLs – Here is a list of best practices: be wary of case sensitivity, hyphens are preferred word separators, Remove/control for unwieldy punctuation characters, including stop words isn’t necessary.
- Multiple Folders URLs – There are too many folders laid out on too many levels. Consider reducing this number as the length of an URL could be a relevant ranking factor.
- Dynamic Parameter URLs – This page’s URL contains too many dynamic parameters. Consider reducing the number of dynamic parameters.
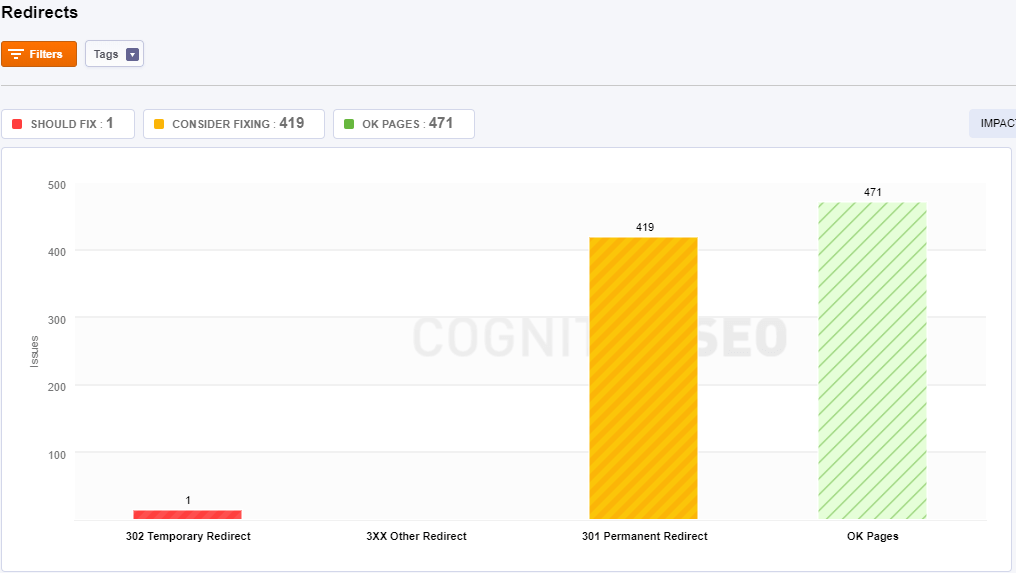
Redirects
URL redirection is a World Wide Web technique for making a web page available under more than one URL address. There are lots of code types of redirection:
- 300 multiple choices;
- 301 moved permanently;
- 302 found;
- 303 see other;
- 307 temporary redirect;
- 308 permanent redirect.
The tool shows you main types of redirects:
- 302 Temporary Redirect: This page is temporarily moved to a different location. The server redirects the site visitor to the new destination despite the original location still being used for requests.
- 3xx Other Redirect: Here you can find some of the redirects we explained above.
- 301 Permanent Redirect: This page has a 301 permanent redirect to another URL. 301 redirects send site visitors to a different URL than the one they originally typed into their browser or selected from a SERP.
Linking Structure
Internal Links
Internal links are links that connect from one page on a domain to a different page on the same domain. Pages with a small number of internal links should be checked, and if required they should be linked from a higher number of pages in your site.
Here are issued the next type of internal links situations:
- Orphan Pages are pages that are not linked to from another section of your site. They cannot be found by search engine crawlers.
- Pages with 1 to 5 internal links are referred by other pages with one to five internal links. An internal link is a type of hyperlink on a webpage to another page or resource, such as an image or document, on the same website or domain.
- Pages with 5 to 10 internal links, Pages with 10 to 20 internal links, Pages with 20 to 50 internal links, Pages with 500 to 100 internal links don’t bring any harm.
- Pages with more than 100 internal links: are an issue. Google recommends keeping the links on a given page under 100).
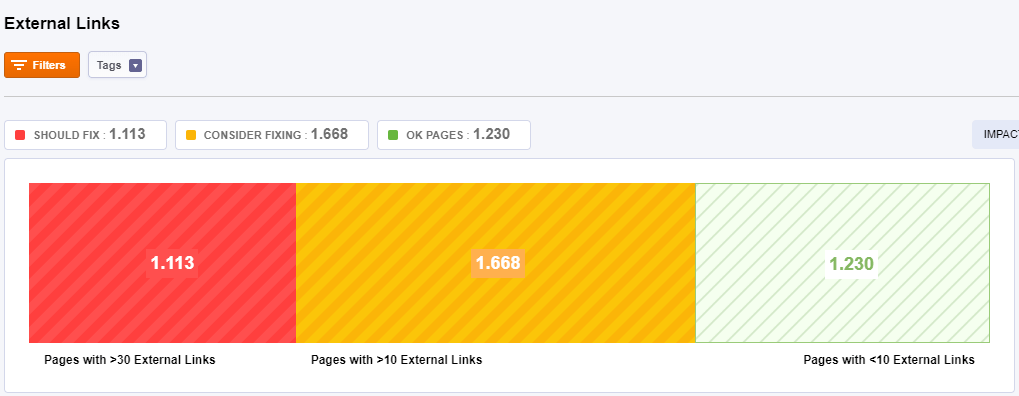
External Links
External links are links that are meant to take you elsewhere. These are hyperlinks that point at any domain other than yours. Most, if not all, websites have external links.
You should check that your pages are not linking out too much or that they are linking to unrelated sites. And for that you can see the next classification:
- Pages with >30 External Links: This page contains more than 30 external links. A high number of external links could be considered an unnatural linking scheme.
- Pages with >10 External Links: This page contains more than ten external links. A high number of external links could be considered an unnatural linking scheme.
- Pages with <10 External Links: No issue associated to these pages.
Nofollow Links
“Nofollow” provides a way for webmasters to tell search engines “Don’t follow links on this page” or “Don’t follow this specific link.”
In this category, you can see the pages with nofollow external and internal links. Just click on the list you’d like to see and you’ll get detailed information about links.
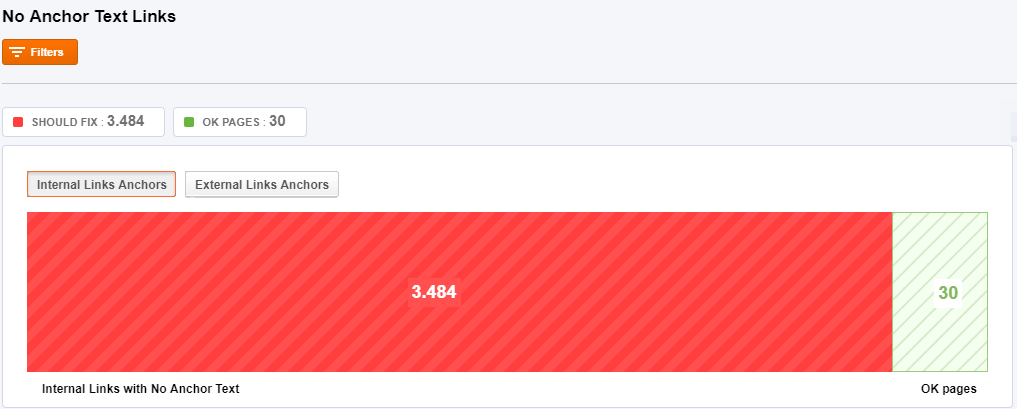
No Anchor Text Links
Google uses anchor text in order to qualify the resources you create a reference to. Not using the appropriate anchor text will make it harder for Google to understand what your pages are about
The red chart shows you pages that contain internal links with no anchor text. The anchor text is the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink. You should check that your pages are correctly linking and use the appropriate anchor text.
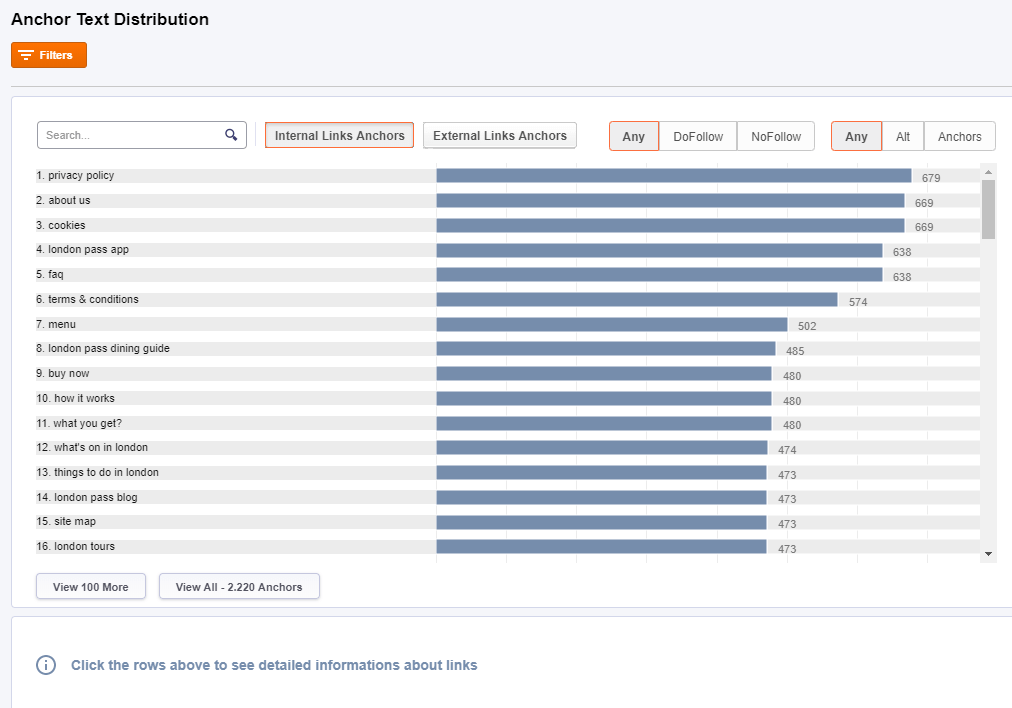
Anchor Text Distribution
The Anchor Text helps people as well as search bots (such as the GoogleBot) to better understand and rank a site. The Anchor Text helps people as well as search bots (such as the GoogleBot) to better understand and rank a site.
Click on the anchor texts displayed on the list will get you detailed information about links:
Click Path
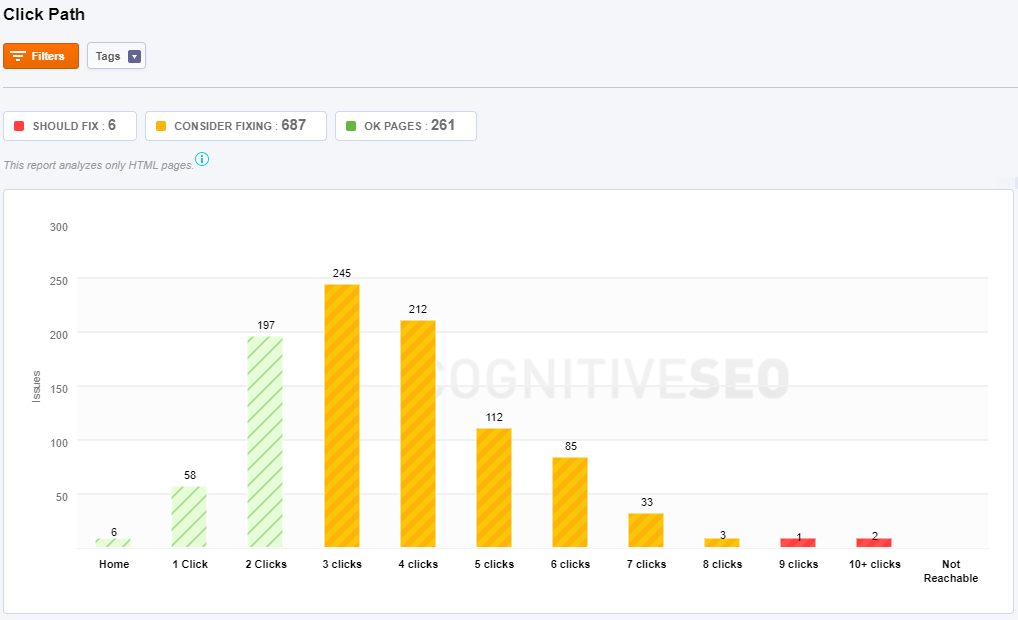
Click Path Analysis allows you to see how visitors may be moving through your website.
Pages that are 3 to 7 clicks away from the homepage are harder to reach while pages that are more than seven clicks away from the homepage may never be reached by a visitor that lands on the homepage.
You can spot the pages that are 9 or more clicks away from your homepage. You need to make them more reachable and link them closer to the homepage.
Broken Links
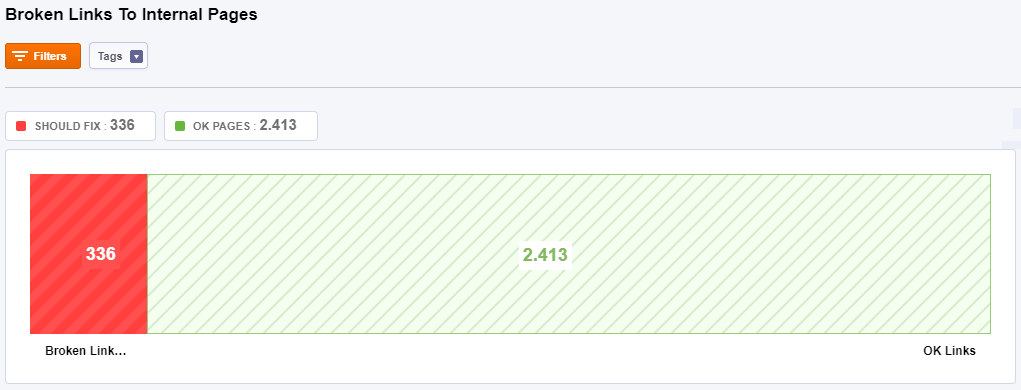
To Internal Pages
A broken link is a link that doesn’t work, often resulting in an error page. A broken link happens when the link points to a webpage that has been deleted or moved. Fighting invalid hyperlinks is a continuous process, so we recommend you to come back and check this page every month.
Checking this section, you’ll be able to see the pages that contain links that are broken and point to external pages. Consider fixing these links.
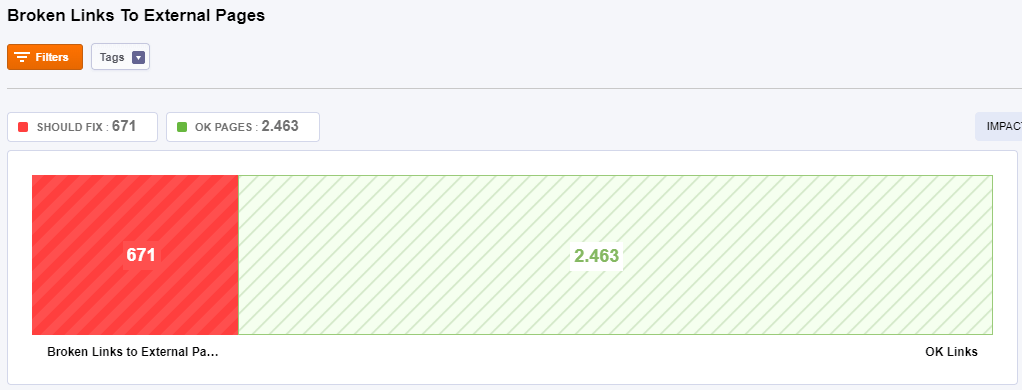
To External Pages
An external broken link is a link from your site to an external resource that doesn’t work, often resulting in an error page. A broken link happens when the link points to a webpage that has been deleted or moved.
Broken Links Negatively Affect SEO as well as the User Experience. Links that are broken will stop search engines from completely indexing your website.
Broken Resources
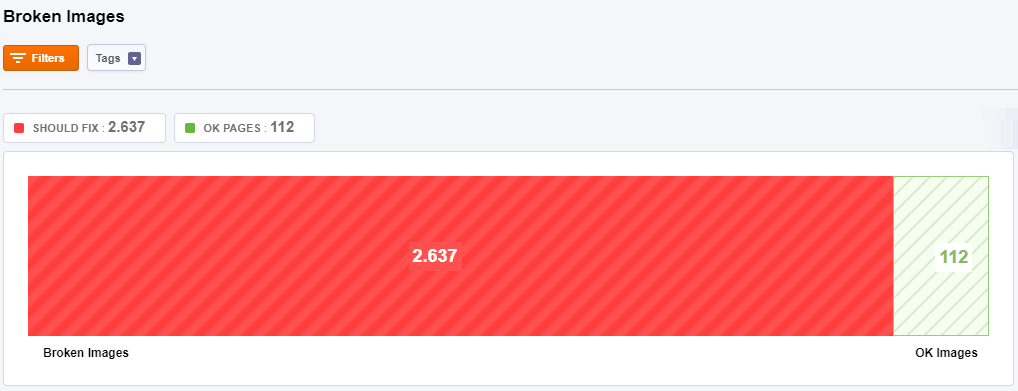
Images
A broken image is considered an image that is linked from a page but can not be loaded. A broken image happens when the tag points to an image that has been deleted. Broken images negatively affect SEO as well as the User Experience.
Multiple broken images will stop search engines from completely indexing your website. You need to verify and fix them.
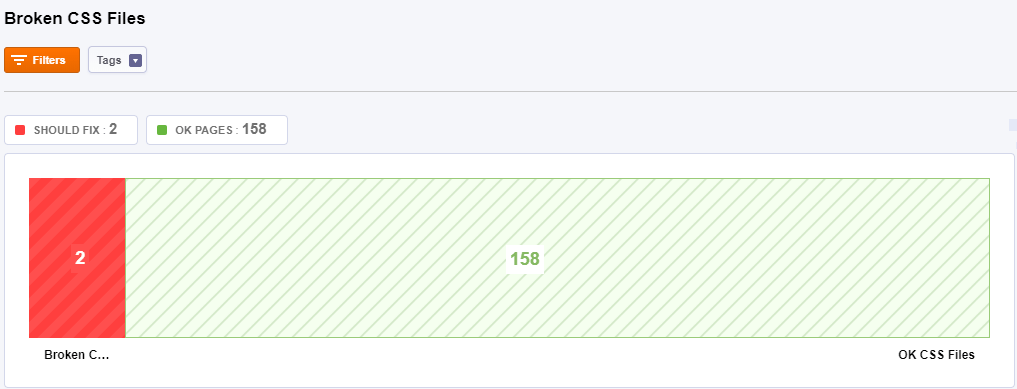
CSS Files
A broken CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) file is considered a stylesheet that is linked from a page but can not be loaded. A broken CSS file happens when the <link rel=”stylesheet”> tag points to an stylesheet that has been deleted. Broken CSS files negatively affect the User Experience. Make sure you check and fix them.
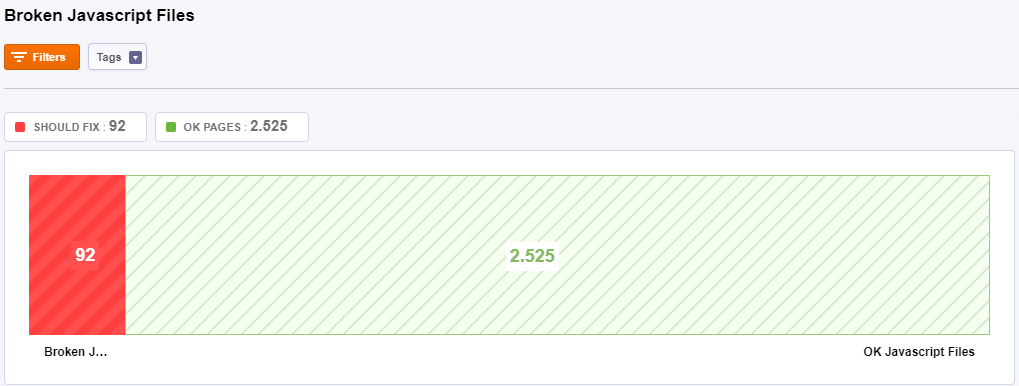
JavaScript Files
A broken JavaScript file is considered a file that is linked from a page but can not be loaded. A broken Javascript file happens when the <script src=”broken-file.js”><script> tag points to a JS file that has been deleted.
Broken Javascript files negatively affect the User Experience as well as SEO.
You could simply delete the broken <script src=”broken-file.js”></script> tag, change the <script src=”broken-file.js”></script> tag to point to a working file or correct the nonexistent file on your site that the <script src=”broken-file.js”></script> tag is currently pointing at.
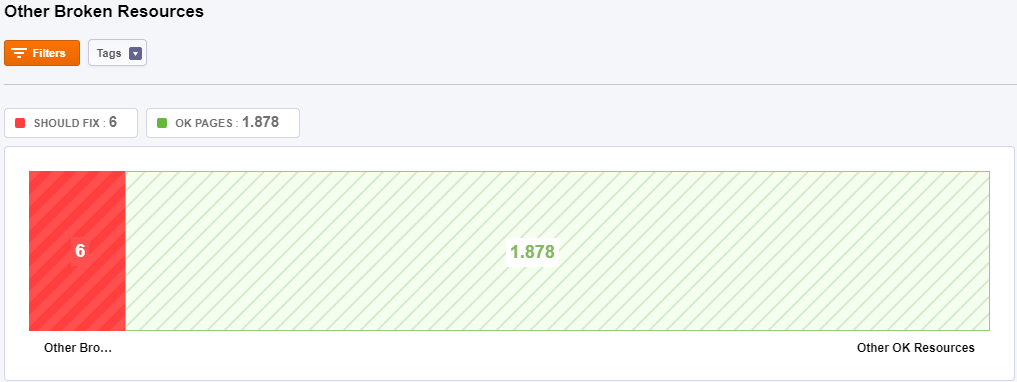
Other
Other broken resource files are considered files that are linked from a page but can not be loaded. The chart shows you the pages that are ok and the ones that contain broken resources.
To identify the broken resource, you need to check the functionality of your site, as resource files might impact your site’s functionality.
Sitemaps
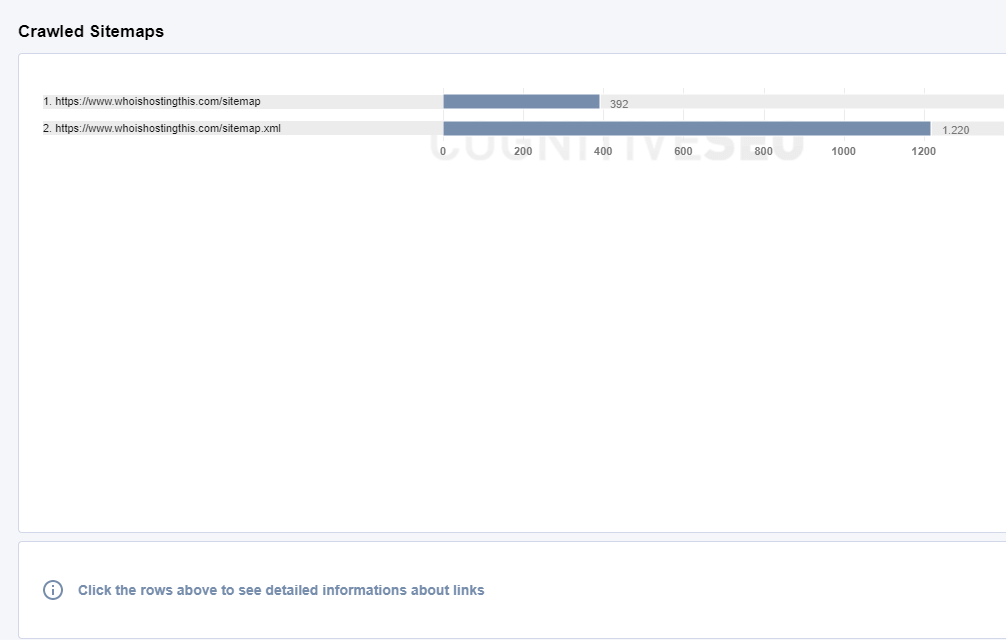
Crawled Sitemaps
A sitemap is a file where you provide information about the pages, videos, and other files on your site, and the relationships between them. A sitemap tells the crawler which files you think are important in your site, and also provides valuable information about these files: for example, for pages, when the page was last updated, how often the page is changed, and any alternate language versions of a page.
Click the sitemap form the list to see detailed information about links:
Included URLs
A sitemap is a file where you provide information about the pages, videos, and other files on your site, and the relationships between them.
Here you can find the URLs that are included in your Sitemap. You can include in your sitemap all the URLs from your site, also the pages that cannot be found other way.
If your site’s pages are properly linked, the web crawlers can usually discover most of your site. Even so, adding all of your URLs to the sitemap can improve the crawling of your site. You can generate your sitemap XML file online. There are lots of free tools that can do that.
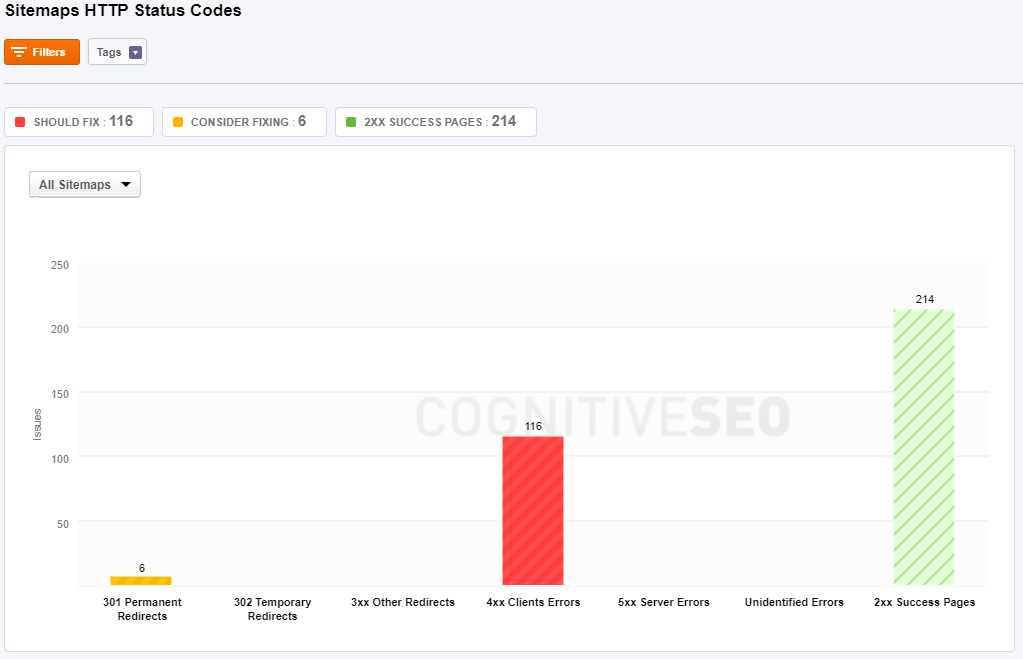
HTTP Status Codes
HTTP Response Status Codes indicate whether a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed.
The tool shows you if a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed. There are 5 HTTP response status codes:
- 1xx (Informational): The request was received, continuing process.
- 2xx (Successful): The request was successfully received, understood, and accepted.
- 3xx (Redirection): Further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request.
- 4xx (Client Error): The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled.
- 5xx (Server Error): The server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request.
Pages that have 301 Permanent Redirects to another URL send site visitors to a different URL than the one they originally typed into their browser or selected from a SERP.
302 Temporary Redirects is a code for pages that are temporary moved to a different location. The server redirects the site visitor to the new destination despite the original location still being used for requests.
3xx Other Redirects include 300, 303-307 redirects. All the pages from this category are moved from an URL to a new source. Depending on the error code you can see the state of the redirection.
4xx Client Errors show pages have one of the 4xx class of status code. This means that the user’s request to access this page contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled.
5xx Server Errors show pages have one of the 5xx class of status code. This means that the server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request of the site’s visitor.
All the pages that the tool couldn’t discover the specific code attached, either it is an incorrect setting or a missing code information, are placed in the Unidentified errors category.
2xx Success Pages have a status code that indicates the client’s request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. These pages don’t have an error; are OK pages.
Mobile
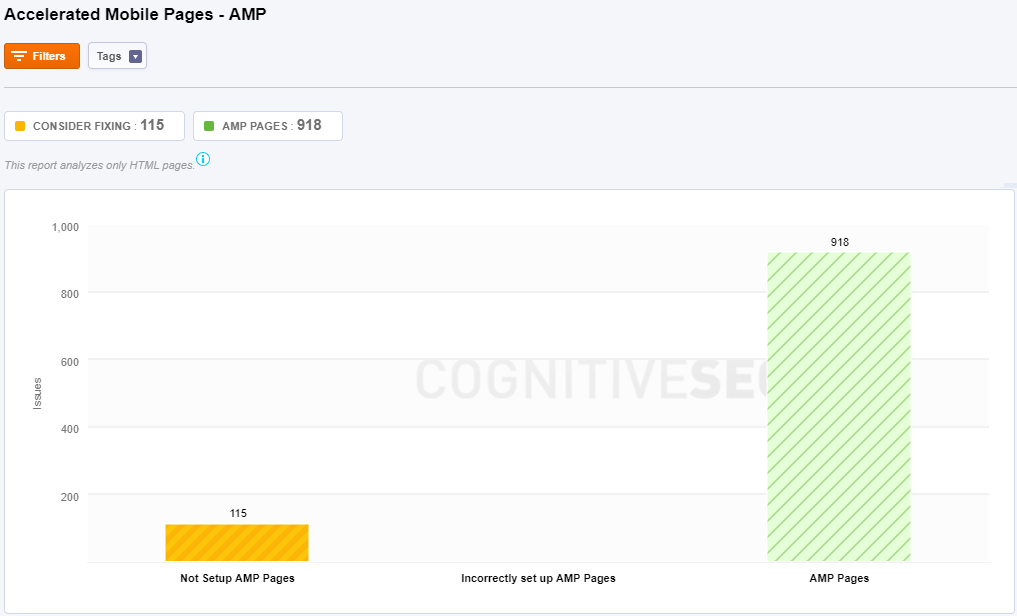
Accelerated Mobile Pages – AMP
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages, a Google-backed project intended as an open standard for any publisher to have pages load quickly on mobile devices. AMP is not directly a search engine ranking factor. However, “speed matters” in search engine ranking.
Site Audit shows the next issues:
- pages that don’t have AMP setup.
- pages that don’t have correctly AMP setup.
Performance
PageSpeed
Page load time is the average amount of time it takes for a page to show up on the screen. Google recommends making web pages fast on all devices. If you haven’t made your website mobile-friendly, you should. The majority of users coming to your site are likely to be using a mobile device.
The tool shows you the next issues:
- Very Slow Pages: All the pages with this issue are loading very slowly.
- Slow Pages: All the pages with this issue are loading slowly.
- Fair Loading Pages: All the pages with this issue are loading OK.
All Data
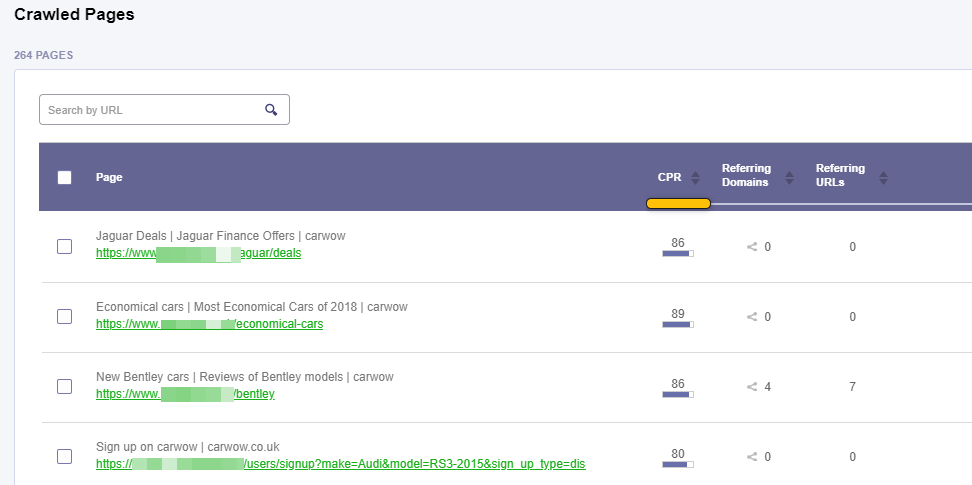
Crawled Pages
Here you can see the list of all the crawled pages for your website.
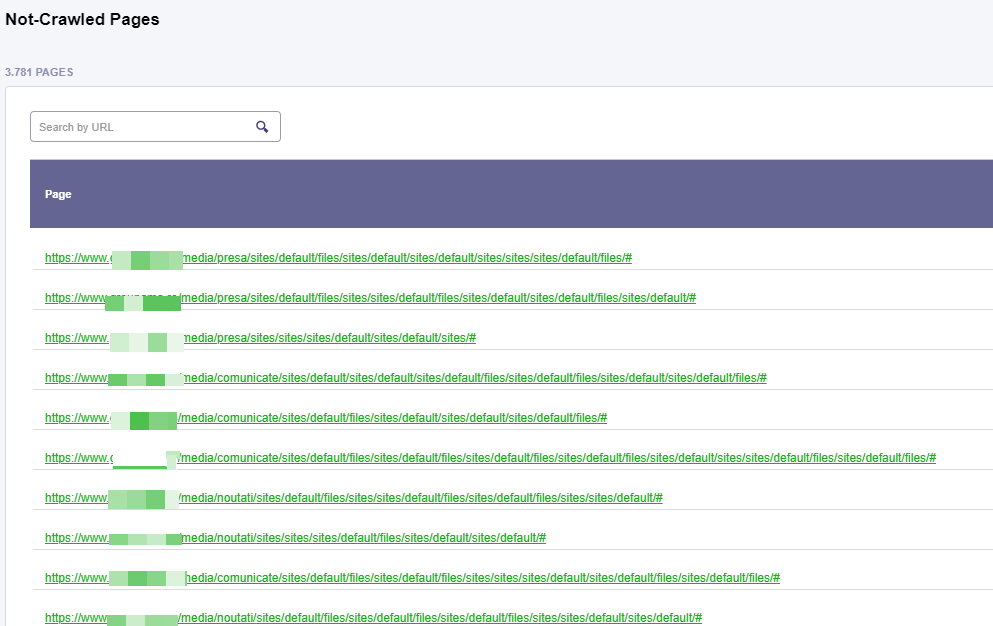
Not-Crawled Pages
Also, you can see the list of not-crawled pages.
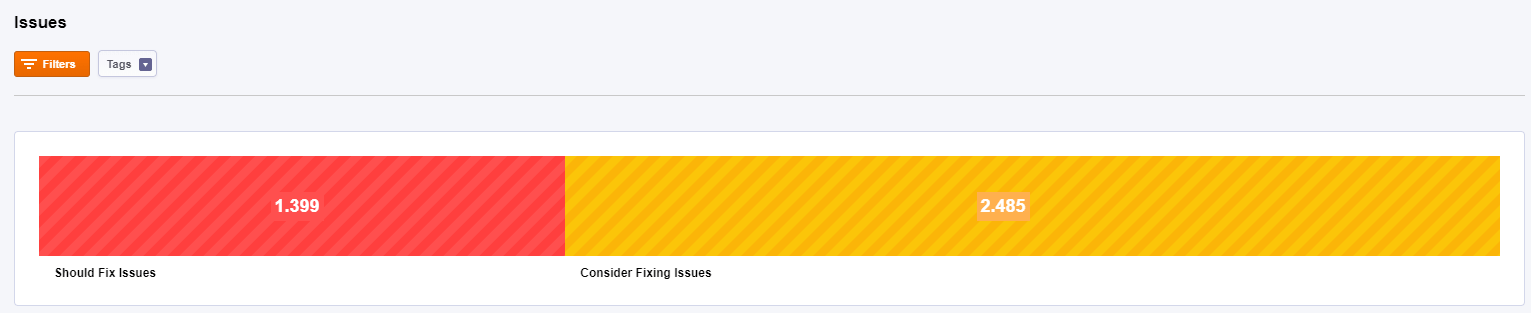
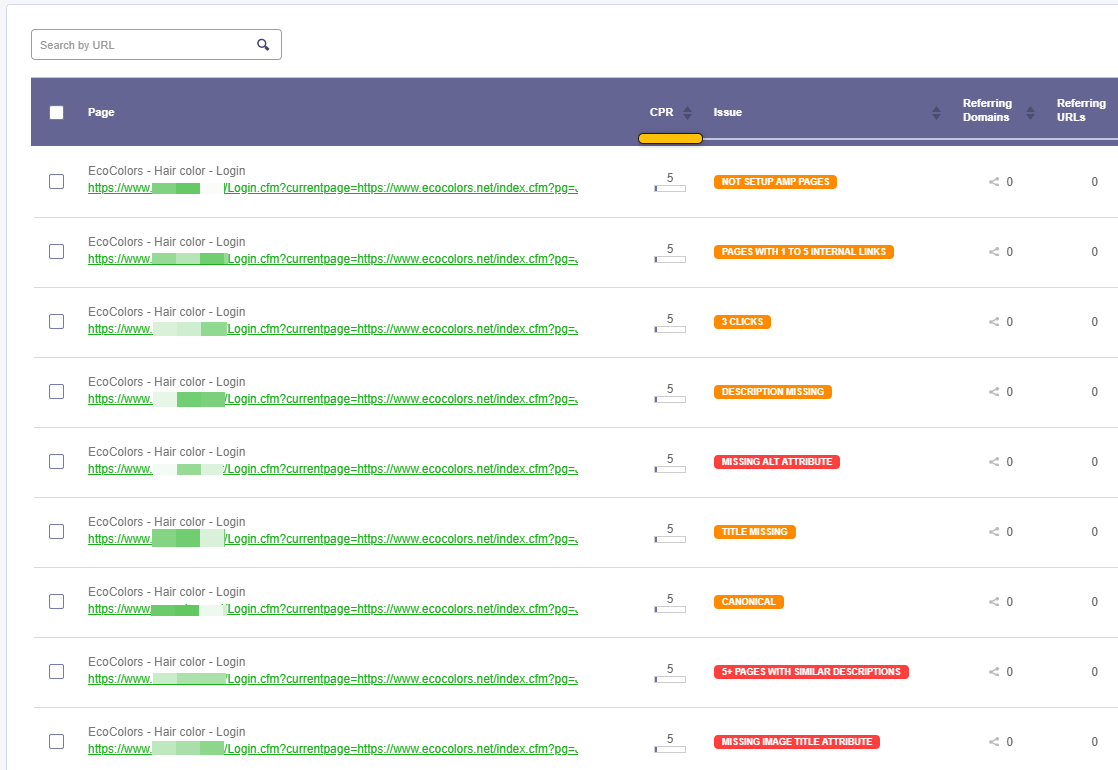
Issues
Here you can see all the pages that issues. They are divided into two main categories: should fix and consider fixing. Click on any of these two sections you’ll see the exact issue for each page
Click on any of these two sections you’ll see the exact issue for each page
Settings
Here you can find the settings area for your campaign. You can edit the options for each website, and enable any tools that you didn’t set up. Click on the tools that you want to setup or edit: Site Audit, Link Analysis, Rank Tracking, Social Media or Google Analytics. Make sure to save the changes at the end.